- Associate degrees
- Cybersecurity certifications
- Cybersecurity bootcamps
- Cybersecurity in Wyoming
- Organizations in Wyoming
- Jobs in Wyoming
This guide contains a brief overview of cybersecurity in Wyoming, including career and educational opportunities. This guide will also cover the economic changes in Wyoming, their outlook, and how they affect the cybersecurity field.
Wyoming’s adoption of cybersecurity brings new prospects to the state’s ranchlands. Its economy primarily focuses on mining excavations for producing coal, natural gas, and oil shale.
Wyoming’s income depends on its mineral production, making the state a precious resource for the country’s capacity for energy, reported the Wyoming Department of Employment.
Ad
cybersecurityguide.org is an advertising-supported site. Clicking in this box will show you programs related to your search from schools that compensate us. This compensation does not influence our school rankings, resource guides, or other information published on this site.
Featured Cybersecurity Degree Programs
| School Name | Program | More Info |
|---|---|---|
| Grand Canyon University | Online BS in Cybersecurity or Online MS in Cybersecurity | website |
| Southern New Hampshire University | Online BS in Cybersecurity or Online MS in Cybersecurity | website |
| Eastern Oregon University | Online BS in Cybersecurity | website |
| UC Berkeley School of Information | Master’s in Cybersecurity | No GRE/GMAT Required | website |
| Purdue University Global | Online BS in Cybersecurity | website |
Among its mining extractions, Wyoming is appropriately named the Cowboy State for its expansive lands suitable for livestock raising, with cattle stock being its dominant resource. Wyoming’s exports include wheat, oats, barley, corn, sugar beets, beans, and potatoes.
About three-fourths of the state’s cropland is regularly irrigated, and much of the state’s production centers around the southeast parts, with only 10,000 farms due to annual precipitation, according to the Department of Agriculture.
However, as a result of the age of the internet, cybersecurity brings an opportunity to the state for fast, dynamic industry and commerce. Wyoming has increasingly relied on information systems to support finances, energy, telecommunications, and emergency response.
Job opportunities for cybersecurity in Wyoming continue to rise as people require security and protection for their information.
Related resources
With the tourism sector at a constant steady influx due to the state’s attractions, such as Yellowstone National Park and Independence Rock, cybersecurity gives way to new opportunities.
While it’s the least populous state in the U.S., according to Forbes, its job growth has been increasing at 1.3 percent, and the federal government owns about half of the landmass of the state.
The federal control over the state’s landmass gives way to a more progressive need for cybersecurity, allowing federal employees to analyze information and implement changes for state-level jurisdiction.
Growing awareness of cybersecurity in Wyoming
The state developed its cybersecurity initiative, Cyber Response and Infrastructure Support Program (CRISP), to shift its focus from purchasing technology to developing cybersecurity services to protect critical data and information systems.
A crucial part of the initiative focuses on incident response and training and has remained a primary focus since 2015.
During the fiscal years of 2017 and 2018, the department adopted the cybersecurity framework for protecting agencies and its stakeholders as a response to the increase of cyber threats to the citizens of Wyoming, according to the Department of Enterprise Technology Services.
The Emersion Data Center holds a data support center and a multi-purpose office building for housing technology and hardware. Now, the state has been consolidating the center, upgrading its power to 480 volts to support its servers and storage hardware.
Through colocation agreements with Wyoming companies, the ETS adopted and revamped the data center to help capitalize on expenditures and upgrade its computing facilities through the Capitol Square Project.
Also, during the fiscal year of 2017-18, the state developed the Risk Assessment Initiative to provide secure computing environments for agencies. This initiative assists agencies in developing their risk assessment plans and puts measurement at the forefront of project planning.
The Wyoming Unified Network continues to expand, allowing agencies to connect and access enterprise resources through its data centers and help reduce the costs of production.
For expanding education, ETS developed the Wyo4Life initiative in 2014, allowing K-12 school districts, community colleges, and universities to use Google Apps for Education to support learning in technology, computing, and cybersecurity.
Secure Cloud through the Wyoming Government Cloud Initiative helps utilize partners such as Microsoft Azure and Silver Star Communications to invest in technology for future generations.
Cybersecurity organizations in Wyoming
Wyoming is a state known for its natural beauty and rugged frontier spirit. But in recent years, the Cowboy State has also become a target for cyberattacks.
As more and more Wyoming businesses and organizations rely on technology, it is more important than ever to take steps to protect against cyber threats.
Fortunately, several cybersecurity organizations in Wyoming can help. These organizations provide a variety of services, including training, consulting, and incident response assistance. They also work to raise awareness of cybersecurity issues and educate the public about how to protect themselves from cyber threats.
Two of the most prominent cybersecurity organizations in Wyoming are:
- CyberWyoming is a non-profit organization that helps Wyoming organizations of all sizes protect themselves from cyber threats. They offer a variety of services, including training, consulting, and incident response assistance. CyberWyoming also leads the Wyoming Cybersecurity Action Network (CAN) Committee, a group of stakeholders from across Wyoming working to improve the state’s cybersecurity posture.
- The CyberWyoming Alliance is a non-profit organization that works to increase cyber awareness and education in Wyoming communities. They offer a variety of programs and services, including presentations, workshops, and resources for businesses and individuals. The CyberWyoming Alliance is also a member of the National Cybersecurity Alliance (NCA), a public-private partnership that promotes cybersecurity awareness and education across the United States.
In addition to CyberWyoming and the CyberWyoming Alliance, several other cybersecurity organizations in Wyoming offer valuable resources and support to Wyoming businesses and individuals. These organizations include:
- The Wyoming Small Business Development Center (SBDC)
- The University of Wyoming (CEDAR)
- The Wyoming Department of Homeland Security
If you are a business owner or individual in Wyoming, there is no excuse not to take steps to protect yourself from cyber threats. The cybersecurity organizations in Wyoming offer a variety of resources and support to help you keep your data safe and secure.
Cybersecurity education in Wyoming
There are several ways to get cybersecurity education in Wyoming. One way is to take a course at a local community college or university. For example, the University of Wyoming offers a cybersecurity certificate program through its College of Engineering and Applied Science.
Another way to get cybersecurity education is to take an online course. Many organizations offer online cybersecurity courses, such as the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) and the National Cybersecurity Alliance (NCA).
In addition to formal education, there are several resources available to help people learn about cybersecurity on their own. The Wyoming Department of Homeland Security has a website with information about cybersecurity threats and how to protect against them.
In 2023, the Wyoming Legislature passed a bill that requires all public schools in Wyoming to teach cybersecurity education to students in grades 6-12.
The bill also requires the Wyoming Department of Education to develop cybersecurity education standards for Wyoming schools.
Cybersecurity associate degrees in Wyoming
Casper College offers an associate’s degree and an associate of applied science in cybersecurity, focusing on business assurance as a marketable asset for job employment and growth. The associate degree is designed to transition students to higher education.
Laramie County Community College offers an Associate of Applied Science in cybersecurity to protect financial information, personal data, and trade secrets. Students learn vulnerability assessments, cryptography, computer security, and information systems analysis.
- Program: A.A.S. in Cyber Security
Credits: 60
Cost per credit: $147 in state | $357 out of state
Delivery method: Campus
Program highlights:- Overview: This program prepares students to protect various sectors from cyber risks.
- Jobs: Trains students for IT support roles.
- Certification: Graduates can earn a CCENT certification.
- Program: Associate of Applied Science in Cybersecurity
Credits: 67
Cost per credit: $154 in state | $364 out of state
Delivery method: Campus, Online
Program highlights:- What's the Program About? LCCC's Cybersecurity program teaches students how to protect online data.
- Courses: Students will learn about computer hardware, operating systems, and advanced security topics.
- Experience: Students get hands-on experience with tools like the Cyber Range and Microsoft Datacenter Academy.
- Program: Associate of Applied Science in Cyber Security
Credits: 61
Cost per credit: $322 in state | $742 out of state
Delivery method: Campus, Online
Program highlights:- Overview: Trains students for jobs in computer and online security.
- Certifications: The program also helps students get ready for well-known security certifications and teaches them to communicate well in the workplace.
- Balanced Curriculum: Mix of technical courses like Linux Basics and soft skills like English and Writing.
Cybersecurity certifications in Wyoming
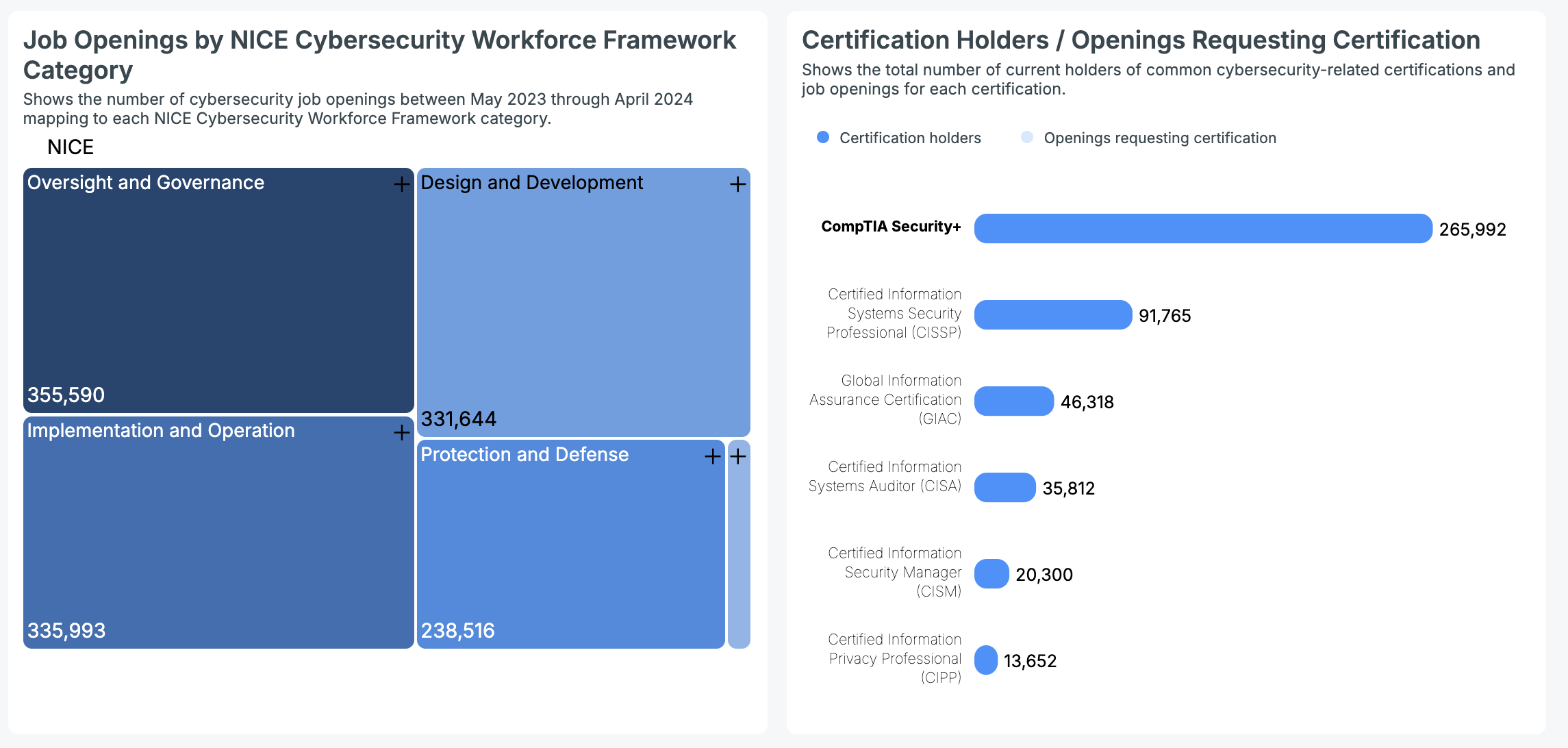
Understanding the current pool of certified cybersecurity talent across the nation is crucial. Cyberseek’s data shows these figures for common certifications:
- CompTIA Security+: 265,992 certification holders
- CISSP: 91,765 certification holders
- GIAC: 46,318 certification holders
- CISA: 35,812 certification holders
- CISM: 20,300 certification holders
- CIPP: 13,652 certification holders
In addition, both Casper College and Sheridan College offer certificates in cybersecurity. Casper College’s Computer Security Certificate allows students to learn the basics in network security, operating systems, Internet networking, and computer forensics for diagnosing, protecting, and preventing computer networking issues.
Sheridan College provides advanced education for cybersecurity, intended for students who have previous training in computer networking and information technology. The certificate narrows down by focusing on threats to computer systems, the laws surrounding computer systems, and fortifying those systems for safety.
- Program: Certificate in Computer Security
Credits: 31
Cost per credit: $147 in state | $357 out of state
Delivery method: Campus
Program highlights:- Purpose: The program trains students to safeguard digital data and computer systems.
- Learning Approach: It combines classroom lessons with hands-on experience.
- CCNA Exam: Finishing the program sets students up to take the CCNA test.
- Program: Cybersecurity Administrator Credit Diploma
Credits: 17
Cost per credit: $154 in state | $364 out of state
Delivery method: Campus, Online
Program highlights:- What: A course for those with some network experience, aiming to start in cybersecurity. It covers topics like protecting networks and databases.
- Jobs: After finishing, you could become a network engineer, IT manager, or similar.
- Transferring: You might be able to use these courses as credits at other colleges.
- Program: Cyber Security Certificate
Credits: 31
Cost per credit: $322 in state | $742 out of state
Delivery method: Campus
Program highlights:- Skill Development: Trains students to detect and counteract threats and vulnerabilities in computer systems.
- Regulatory Insight: Provides understanding of computer security laws and how to remain compliant.
- Audience: Tailored for students in the Computer Network Administration AAS and existing IT professionals.
- Program: Cybersecurity Certificate
Credits: 20 hours
Cost per credit: $166 in-state | $692 out of state
Delivery method: Campus
Learn more: Program details
Cybersecurity bootcamps in Wyoming
- Program: Cybersecurity Boot Camp
Credits: 24 weeks
Cost per credit: $12,995
Delivery Method: Online
Learn more: Program details
Cybersecurity jobs in Wyoming
As supercomputers and several data centers plant themselves throughout the state, the a need for cybersecurity professionals to continue expanding networks and technology to schools and other areas.
The slow downturn of the state’s energy sectors reinforces the need for technology-based jobs. The state’s advancements in early-education computer science allow for technology firms to expect steady employment for future infrastructure and development.
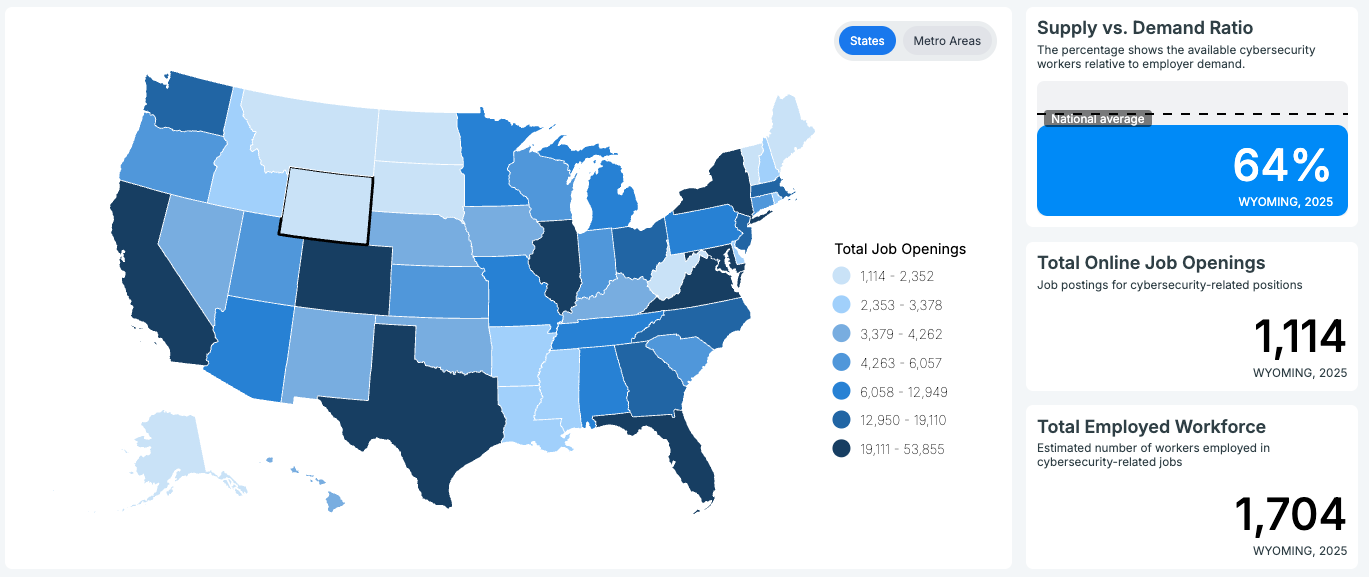
Cyberseek’s data shows a total of 1,114 job openings in Wyoming, and about 1,704 people maintained employment in the cybersecurity sector from May 2023 through April 2024.
Additional observations in the cybersecurity field include:
Supply: The workforce supply/demand ratio is 64 percent.
Certifications State and employer requirements for employment demonstrate a need for competence in certifications such as CompTIA Security+, Global Information Assurance Certification (GIAC), and Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP).
Some of the top job titles for current employees include:
- Cyber Security Engineer
- Vulnerability Analyst / Penetration Tester
- Cyber Security Analyst
- Network Engineer / Architect
- I.T. Specialist / Engineer
- Cyber Security Consultant
Cybersecurity in Wyoming
The U.S. cybersecurity hiring market pulsed with significant demand from May 2023 to April 2024. Nationwide, Oversight and Governance roles were at the forefront with 355,590 openings.
Implementation and Operation (335,993) and Design and Development (331,644) also fueled this demand. Protection and Defense roles tallied 238,516, and Investigation roles, while fewer still represented 19,525 opportunities.
Wyoming’s transition from mining and livestock to information technology currently moves slowly in the state’s economy. Still, it will dynamically impact the living situations of its citizens in a matter of years.
While Wyoming has not made drastic changes to its business sectors, its focus on education programs and cybersecurity initiatives helps to increase potential value for incoming firms in need of data security measures.
Digital technology continues to turn over the vast lands of agriculture and energy production in exchange for business infrastructure and financial growth. Data has become essential for companies to communicate, exchange, analyze, and track the supply and demand of their services.
Cybersecurity helps maintain these transactions and can provide future employment for new generations.