- Associate degree
- Bachelor’s degree
- Master’s degree
- Cybersecurity certifications
- Cybersecurity in Arkansas
- Jobs in Arkansas
This guide is all about cybersecurity in Arkansas, including some of the state’s major cybersecurity-related educational and career opportunities.
Walmart is one of the largest employers in the United States. The retail giant, worth $514 billion, according to Forbes in 2019, has its corporate headquarters in Arkansas.
Ad
cybersecurityguide.org is an advertising-supported site. Clicking in this box will show you programs related to your search from schools that compensate us. This compensation does not influence our school rankings, resource guides, or other information published on this site.
Featured Cybersecurity Degree Programs
| School Name | Program | More Info |
|---|---|---|
| Arkansas State University | Online BS in Digital Technology - Cloud Computing & Cybersecurity | website |
| Purdue Global | Online BS in Cybersecurity | website |
| UC Berkeley School of Information | Master’s in Cybersecurity | No GRE/GMAT Required | website |
| Grand Canyon University | Online BS in Cybersecurity or Online MS in Cybersecurity | website |
| Utica University | Online BS in Cybersecurity | website |
| Southern New Hampshire University | Online BS in Cybersecurity or Online MS in Cybersecurity | website |
Despite Arkansas’ recent lack of innovation in the high-tech sector, its low business costs make it an attractive destination for companies in the service and tech industries.
However, this lack of innovation has also contributed to Arkansas’ ranking as the 6th worst state economy in the country, according to WalletHub, based on GDP growth, annual household income, exports per capita, and unemployment rate.
Arkansas has several key industries that contribute to its economic development, including distribution and logistics, aerospace and defense, and corporate and shared services.
The software development and data management services sectors employ 1.3 million people in the state, making them the largest employers in Arkansas.
Related resources
LiveRamp Holdings, Inc. provides Arkansas with more than 1 trillion transactions for more than 7,000 global clients, and Hewlett-Packard chose Arkansas for its large customer support center and regional industry development center.
Arkansas homes numerous technology firms, including Little Rock Technology, Genesis Technology Incubator, and The Venture Center.
Arkansas’s long-term goals projections help facilitate cybersecurity initiatives, all driven by government legislature and corporate globalization, to revolutionize the state into a place of commercial and technological magnitude.
Growing awareness of cybersecurity in Arkansas
Former Arkansas Governor Asa Hutchinson recently signed into law a cybersecurity initiative, enforcing the state’s Economic Development Commission (AEDC) to develop a robust defensive strategy against cyber attacks.
Through Senate Bill 632, the public will gain education opportunities related to cybersecurity and defense, corporate enterprises will be provided with threat assessments and other initiatives around technology and security.
The State of Arkansas Cybersecurity Office coordinates regional resources to protect government operations and establishes cybersecurity policies for information technology services.
The office collaborated with the National Cybersecurity Alliance to develop the “Stop. Think. Connect.” campaign
As a national public awareness effort to increase awareness of cyber threats and promote safer online activity.
Arkansas’s cybersecurity initiatives resulted in its Arkansas eGovernment an accessible platform for thousands of IT users and management services.
Its Division of Information Systems has connected 200+ professionals and provided them with equipment hosting, network, and professional services.
Some of the services the office provides for enterprises include monitoring router and server security, monitoring networks for server and router vulnerabilities, and assisting customers with router and server security tools.
The Division of Information Systems also developed virtual private networks, allowing individuals to seek secure remote access to state computing resources and information.
Here is a list of some of the key cybersecurity organizations and entities in Arkansas:
- Arkansas State Fusion Center (ASFC): Operated by the Arkansas Department of Emergency Management, the ASFC functions as a central point for the gathering, analysis, and dissemination of threat-related information.
- Arkansas Tech University Cybersecurity Institute: Offers education and training in cybersecurity, aimed at preparing students to address current and emerging cyber threats.
- University of Arkansas at Little Rock (UALR) Cyber Gym: Provides hands-on cybersecurity education and training for students and professionals, simulating real-world cybersecurity scenarios.
- Arkansas Office of Information Technology: Tasked with securing the state’s digital infrastructure, this office handles cybersecurity policy for Arkansas’s state government resources.
- The Cybersecurity Center for Business at the University of Central Arkansas: Dedicated to assisting businesses with cybersecurity needs, providing risk assessments, training, and resources to help protect Arkansas businesses from cyber threats.
- The Arkansas Small Business and Technology Development Center (ASBTDC): Offers resources to help small businesses in Arkansas, including training and consulting on cybersecurity best practices.
- InfraGard Arkansas Members Alliance: Affiliated with the FBI, this alliance brings together representatives from the private sector, public sector, and academia to share information about physical and cybersecurity threats and best practices.
- Arkansas Cyber Alliance: Collaboration between educational institutions, private businesses, and the government to promote cybersecurity awareness and develop initiatives to enhance the state’s cybersecurity workforce.
- Cybersecurity Association of Arkansas (CyberArk): A professional association that provides networking and professional development opportunities for cybersecurity professionals in Arkansas.
Cybersecurity education in Arkansas
Arkansas provides its citizens with several avenues for earning an education in cybersecurity, supplying students with the capabilities and resources to receive valuable careers in the information technology field.
Arkansas Inc., a business venture of the Arkansas Economic Development Commission, serves as a supervisory tool for diversifying the state’s economy through investments and job developments.
Some of the milestones the venture provided for the state include the Emerging Analytics Center (EAC) at the University of Arkansas Little Rock, which offers data analytics and data visualization to give solutions for big data.
The venture also implanted research competencies in high-performance computing at the University of Arkansas in Fayetteville.
Cybersecurity associate degrees in Arkansas
For students looking for a career in cybersecurity, associate degrees offer the chance to learn the basics of firewall protection methods, software applications, decoding sensitive data information, and techniques against security breaches.
- Program: Associate of Applied Science in Cybersecurity
CAE designation: CAE-CD
Credits: 60
Cost per credit: $239 in state | $278 out of state
Delivery method: Campus
Program highlights:- Goal: Train students to both hack and protect computer systems.
- What You'll Learn: Basics of coding, wireless tech, math, and network setup. The course blends theory with hands-on practice.
- Course Content: Encompasses courses in programming, wireless technologies, mathematics, and networking.
- Program: AAS in Computer Information Systems - Option Networking
Credits: 66
Cost per credit: $79 in state | $164 out of state
Delivery method: Campus
Program highlights:- Jobs: Graduates can work as computer technicians, network administrators, help desk analysts, and more.
- Accreditation: The college's computer programs, except for CAD, are accredited by a recognized council since 2014.
- Additional Certifications: Provides a technical certificate in networking and cyber security.
Cybersecurity bachelor’s degrees in Arkansas
Bachelor’s degrees provide progressive preparation in cybersecurity degrees, allowing students to learn to apply cybersecurity methods in network security, information systems, advanced web development, and software development.
The University of Arkansas offers a minor in computer science and a minor in cybersecurity, teaching the basics of programming foundations and programming models. Southern Arkansas University’s bachelor of science degree in computer science has a specific focus on cybersecurity defense.
Campus-based bachelor’s degree
- Program: Bachelor of Science in Computer Science – Privacy and Cyber Security Option
Credits: 120
Cost per credit: $240 in state | $426 out of state
GRE/GMAT Required: Not Required
Delivery method: Campus, Hybrid
Program highlights:- Overview: Students learn both theory and practical skills to tackle cyber threats and ensure privacy. The program also covers the latest trends in these fields.
- Specialized Subjects: Privacy Engineering, Cyber Forensics, and Cyber Defense.
- Note: No need to choose a minor subject.
- Program: Bachelor of Science in Cybersecurity
Credits: 120
Cost per credit: $250 in state | $500 out of state
GRE/GMAT Required: Not Required
Delivery method: Campus
Program highlights:- Course Aim: Understand online threats and how to defend against them.
- Subjects: Learn to create secure networks and understand hacking methods.
- Feedback: Most graduates see the degree as a good investment.
- Program: Bachelor of Science in Cybersecurity
CAE designation: CAE-CD
Credits: 120
Cost per credit: $235 in state | $635 out of state
GRE/GMAT Required: Not Required
Delivery method: Campus
Program highlights:- Expert Teachers: The program's teachers have real-world experience and are dedicated to helping students learn about cybersecurity.
- Practical Training: Students can practice their skills in the Trojan Cyber Arena, a safe online space.
- Job Opportunities: Cybersecurity jobs are in high demand, with a median salary of $112,000 in 2022.
Online bachelor’s degree
- Program: Bachelor of Science in Computer Science – Privacy and Cyber Security Option
Credits: 120
Cost per credit: $240 in state | $426 out of state
GRE/GMAT Required: Not Required
Delivery method: Campus, Hybrid
Program highlights:- About the Program: Students learn the theory behind cyber security and get practical training to stop cyber threats.
- Overview: Offers students a dual and complementary expertise in cyber security and privacy.
- Program Study: They will study how to make systems that respect user privacy.
Cybersecurity master’s degree in Arkansas
Master’s degrees focus primarily on honing the skills needed in cybersecurity leadership, researching and informing the public of the most current digital methods of protection and innovation.
At Southern Arkansas University, students can earn a Master of Science degree in Computer and Information Science with a cybersecurity and privacy option. Through this degree program, students will learn applicable and theoretical methodologies in computer science.
Master’s program listings
- Program: Master of Science in Computer and Information Science – Cyber Security and Privacy Option
Credits: 30
Cost per credit: $312 in state | $490 out of state
GRE/GMAT Required: Not Required
Delivery method: Online
Program highlights:- Cyber Security Track: Learn about online safety, data protection, and privacy rules.
- Coursework: 30 hours of classes, including core subjects and specialized Cyber Security courses, plus elective options.
- Overview: Southern Arkansas University offers a Master's program in Computer Science, which is both affordable and comprehensive.
- Program: Master of Science in Information Systems (MSIS) - Computer Security Management
Credits: 30
Cost per credit: $830
GRE/GMAT Required: Not Required
Delivery method: Online
Program highlights:- Course Content: Learn to defend against hackers, design firewalls, and understand security tools.
- Accreditation: Recognized by the Middle States Commission on Higher Education.
- Alumni Views: 75% of graduates found the degree valuable, based on a 2021 survey.
- Program: Online Master of Science in Information Security and Assurance
Credits: 30
Cost per credit: $830
GRE/GMAT Required: Not Required
Delivery method: Online
Program highlights:- Certifications: The program prepares students for specific industry exams.
- Meets U.S. Standards: It follows U.S. guidelines for cybersecurity training.
- About the Program: Teaches students how to protect against cyber threats.
Cybersecurity certifications in Arkansas
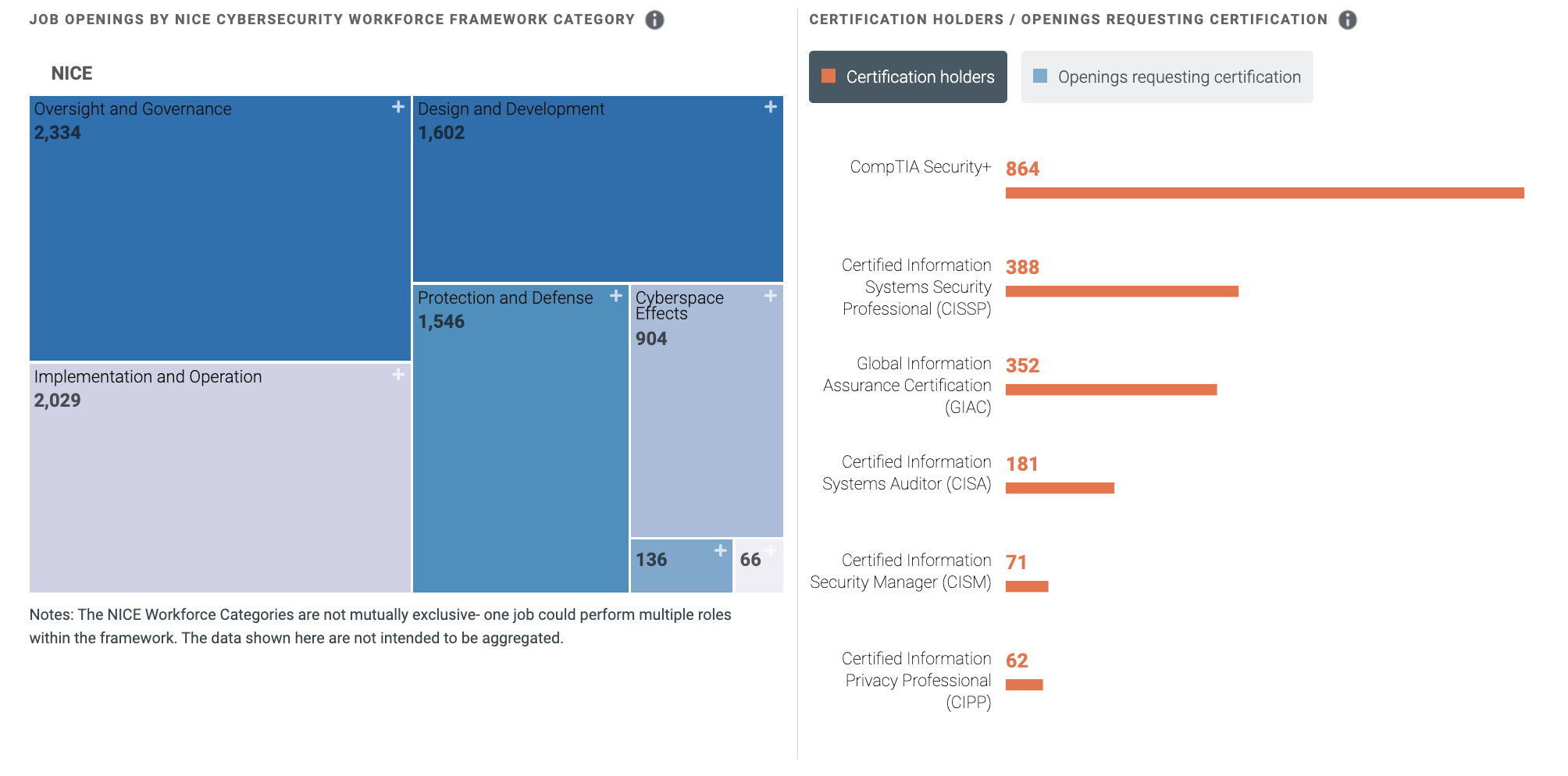
The graduate certificate focuses on courses related to computer security, database security, secure digital systems design, and advanced cryptography. Here is a list of programs:
- Program: Technical Certificate in Networking and Cyber Security
CAE designation: CAE-CD
Credits: 34
Cost per credit: $79 in state | $164 out of state
Delivery method: Campus
Program highlights:- Skills: Students learn to design, set up, and fix computer networks.
- Certifications: The course prepares students for various IT exams like CCNA and CompTIA.
- Jobs: Graduates can become computer technicians, network admins, and other IT roles.
- Program: Cybersecurity Graduate Certificate
CAE designation: CAE-R
Credits: 12
Cost per credit: $219 in state | $595 out of state
Delivery method: Campus
Program highlights:- Overview: Aims to provide students with the expertise to defend crucial data and hone a diverse set of security skills to anticipate and counteract cyber threats.
- Program: The institution emphasizes research, academics, and campus life, with a strong presence on various social media platforms.
- Events: The university also hosts various events and news updates, including wellness programs and employee spotlights.
- Program: Cybersecurity Advanced Technical Certificate
CAE designation: CAE-CD
Credits: 29-30
Cost per credit: $345 in state | $740 out of state
Delivery method: Campus
Program highlights:- Program: The certificate offers a mix of tech-focused and ethical courses, ensuring a comprehensive cybersecurity education.
- Overview: Its structure is adaptable, catering to both immediate entry into the cybersecurity domain and those planning a longer academic route.
- Key Takeaway: The emphasis on ethics highlights the significance of ethical decision-making in cybersecurity operations.
- Program: Cybersecurity Fundamentals Certificate of Proficiency
CAE designation: CAE-CD
Credits: 11-12
Cost per credit: $345 in state | $740 out of state
Delivery method: Campus
Program highlights:- Courses: Students will learn about computing, security, and ethics.
- Program: The course is short, just 11-12 hours.
- For Beginners: It's a great start for a cybersecurity career or to add to what an individual knows.
- Program: Technical Certificate in Cybersecurity
Credits: 21
Cost per credit: $84 in state | $125 out of state
Delivery method: Campus
Program highlights:- Overview: Provides an in-depth study of cybersecurity, touching on various critical areas from safeguarding networks to understanding digital ethics.
- Experience: Enrolled students will be equipped with the necessary skills and knowledge to navigate the dynamic landscape of cybersecurity.
- Computer Ethics: Courses will help shape the perspective ethics of cybersecurity professionals.
- Program: Certificate of Proficiency in Cybersecurity Fundamentals
Credits: 12
Cost per credit: $84 in state | $125 out of state
Delivery method: Campus
Program highlights:- Credit Structure: The entire program is designed to be completed in 12 credits, ensuring a concise yet comprehensive understanding of the subject matter.
- Core Curriculum: The program is structured around four primary courses, each contributing to the comprehensive understanding of cybersecurity.
- Program Department: The course is affiliated with the Computer Information Systems department, indicating a strong foundation in both computer systems and their security aspects.
Cybersecurity jobs in Arkansas
Arkansas, despite its recent ratings in unemployment, plans to increase the number of cybersecurity jobs within the state by 2026. The surge of tech enterprises situating their facilities and offices within the state allows for cybersecurity jobs to grow substantially.
The state’s focus on its cybersecurity initiatives provides for the state to focus on protecting government data, communicate globally with high-enterprise institutions, and establish new education programs for computer science and cybersecurity.
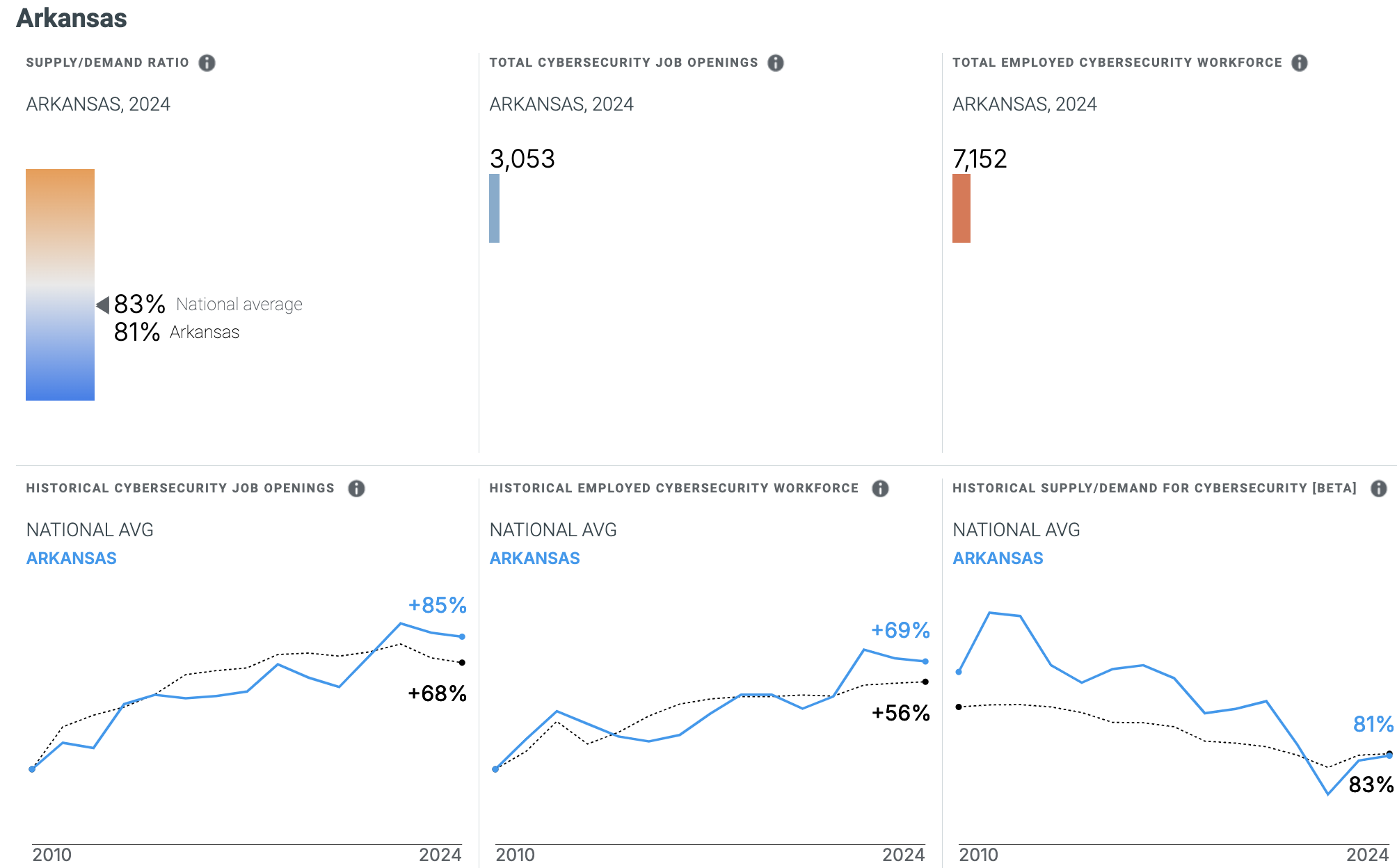
With a total of 3,053 current job openings in Arkansas, roughly 7,152 employees currently work in the cybersecurity field, according to Cyberseek.
The average hourly wage for a cybersecurity analyst in Arkansas is $44.79, with the annual average wage at $93,150 in 2023, according to the Bureau of Labor Statistics data.
Cybersecurity in Arkansas
Arkansas has grown from being the king of cotton and agriculture to a center of finance, manufacturing, and software development.
Arkansas now strives to expand its cybersecurity initiatives as it anticipates a massive influx of tech companies for the next ten years.
As tech companies begin to establish their headquarters and offices in the state, the state’s unemployment rate will theoretically decline, bringing in more cybersecurity jobs as a result.