- Associate degrees
- Bachelor’s degrees
- Master’s degrees
- Cybersecurity certifications
- Cybersecurity jobs
- Related resources
This guide is about some of the many cybersecurity schools in Kentucky as well as some of the cybersecurity-related career opportunities available in the state.
Accounting for one of every six jobs in the state, manufacturing is one of the backbones of Kentucky’s economy. There are roughly a quarter million manufacturing jobs in the state, the result of 6,000+ manufacturing facilities.
Ad
cybersecurityguide.org is an advertising-supported site. Clicking in this box will show you programs related to your search from schools that compensate us. This compensation does not influence our school rankings, resource guides, or other information published on this site.
Featured Cybersecurity Degree Programs
| School Name | Program | More Info |
|---|---|---|
| Purdue Global | Online BS in Cybersecurity | website |
| Southern New Hampshire University | Online BS in Cybersecurity or Online MS in Cybersecurity | website |
| Northern Kentucky University | Online BS in Information Technology - Cybersecurity | website |
| UC Berkeley School of Information | Master’s in Cybersecurity | No GRE/GMAT Required | website |
| Grand Canyon University | Online BS in Cybersecurity or Online MS in Cybersecurity | website |
Those manufacturing plants produce a lot of products and Kentucky exported $34.4 billion of Kentucky-made products, a new record. Those numbers, and the increase in exports over the years, make Kentucky a larger exporter than the entire country of Greece.
While Canada is Kentucky’s largest trade partner, their exports make their way to almost two hundred countries each year. The largest category of manufactured export is aerospace products.
Manufacturing doesn’t tell the whole story, however. There is another multi-billion dollar industry in Kentucky that thrives due to the state’s advantageous geography.
Kentucky isn’t dead center in the United States, however, it is nearly perfectly centered when accounting for population. That has led to the development of a massive shipping and logistics industry, an industry unapparelled anywhere in the world.
Take package sorting, for example. “The UPS Worldport at Louisville International Airport is the largest fully automated package-handling facility in the world.” That facility processes about 1.5 million packages a day, or put differently, 17.4 packages a second.
That’s a lot of packages and it represents the work of just one company. DHL also has a facility in Kentucky that recently underwent a $100 million expansion. FedEx is also expanding its in-state operation.
While impressive, these facilities have a weakness. By necessity, they’re heavily automated. What’s automated is susceptible to cyberattack and even though disrupting America’s package supply might not be the first order of business for a cybercriminal, the threat is real enough.
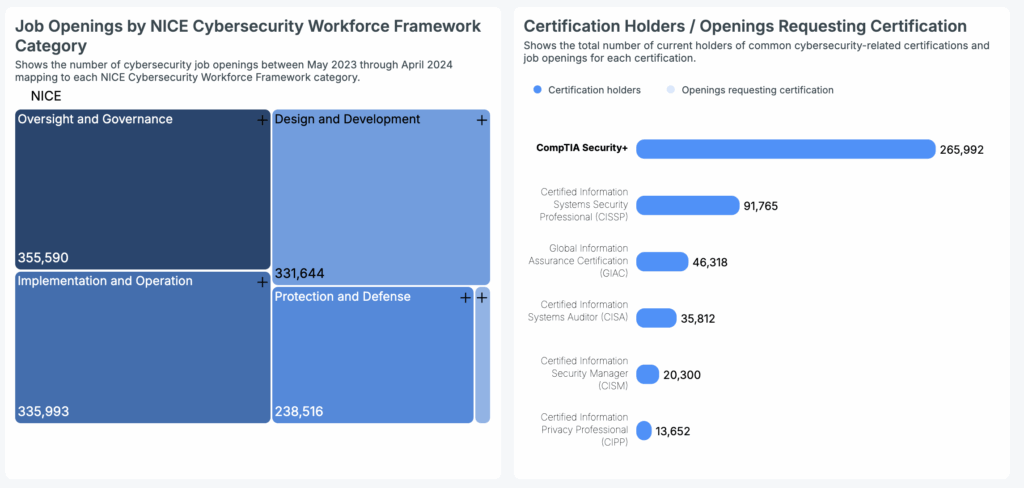
Analyzing cybersecurity U.S job trends from May 2023 to April 2024 reveals significant demand. Oversight and Governance had the highest number of openings (355,590). Implementation and Operation and Design and Development were also in high demand, with 335,993 and 331,644 positions respectively. Protection and Defense roles totaled 238,516, while Investigation roles comprised 19,525.
Thankfully, Kentucky is aware of the important role that cybersecurity plays in this computer-powered age. Through conferences and state-driven initiatives, they’re seeking to promote cybersecurity awareness and find solutions to today’s most pressing digital problems.
Cybersecurity in Kentucky
The Cyber Security Conference has become an annual event in Kentucky. Designed especially for enterprise IT employees, as well as government security technicians, the conference is a chance to learn about the latest cybersecurity threats and how to combat them.
Attendees can also learn about compliance; ensuring that their company’s digital systems are fully compliant with the latest regulations.
In addition to the conference, Kentucky’s legislator recently passed KY HR 171, “A resolution urging a comprehensive study of and subsequent plan to deal with the growing blockchain technology.”
What’s interesting is that instead of vilifying cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology, as many have done, the state of Kentucky acknowledges their potential.
“These advances in blockchain technology have great potential in the area of economic development as many innovative startups and entrepreneurs have entered the blockchain sector.”
The legislation does recognize, however, that without proper oversight and regulation, blockchain and cryptographic currencies may do more harm than good.
Finally, the National Security Agency and the Department of Homeland Security recently named Kentucky’s Owensboro Community & Technical College’s computer and information technology program a National Center of Academic Excellence in Cyber Defense Education.
The designation recognizes the program’s high standard of teaching regarding cybersecurity and cyber defense. It illustrates the focus that Kentucky places on cybersecurity education. Indeed, they have several cybersecurity programs available to potential students.
Cybersecurity education in Kentucky
Educating people about cybersecurity is important in Kentucky, as it helps them learn how to defend important computer systems and data. As cyberattacks become more common, it’s vital to have trained people ready to protect the private information of individuals, businesses, and the government.
Also, as Kentucky’s economy gets bigger, especially in areas like healthcare, manufacturing, and moving goods around, strong cybersecurity is even more important.
This makes teaching cybersecurity a key part of keeping Kentucky safe and successful in the future.
Related resources
Cybersecurity associate degrees in Kentucky
While an associate’s degree may limit the number of cybersecurity jobs that a graduate will be able to apply for, the two-year degree has the advantage of being less expensive than a bachelor’s.
Currently, Kentucky has two schools that offer associate’s degrees: Bluegrass Community and Technical College and Owensboro Community and Technical College.
- Program: AAS in Cybersecurity
CAE designation: CAE-CD
Credits: 61-64
Cost per credit: $186 in state | $250 out of state
Delivery method: Campus & online
Learn more: Program details - Program: Associate in Applied Science in Information Security Track
CAE designation: CAE-CD
Credits: 60-64
Cost per credit: $186 in state | $250 out of state
Delivery method: Campus
Learn more: Program details
Cybersecurity bachelor’s degrees in Kentucky
A bachelor’s degree is a great choice as most cybersecurity jobs require a four-year degree or higher. A bachelor’s program will prepare students to recognize and neutralize many of the most common types of cyber threats.
In addition, students may study subjects outside of the IT field like history or English literature.
Campus-based cybersecurity bachelor’s degrees
Kentucky currently offers three cybersecurity bachelor’s degree programs. Please see the following list for more information.
- Program: B.S. in Network Security and Electronics
Credits: 120
Cost per credit: $318 in-state | $357 out-of-state
Delivery method: Campus
Learn more: Program details - Program: Bachelor of Science in Computer Science – Computer Information Security Option
Learn more: Program details - Program: Bachelor of Science in Cybersecurity
Credits: 180
Cost per credit: $420
Delivery method: Campus & online
Learn more: Program details
Online cybersecurity bachelor’s degrees
The main advantage of an online degree is flexibility. With an online degree, it’s easier to study while working, making this an ideal way for someone to earn an income while also furthering their education.
Students in Kentucky can choose from four online bachelor’s degree programs.
- Program: Bachelor’s in Computer Information Systems - Cybersecurity concentration
Credits: 120
Cost per credit: $624
Delivery method: Online
Learn more: Program details - Program: Bachelor's in Information Technology - Concentration Information Security
CAE designation: CAE-CD
Credits: 120
Cost per credit: $335
Delivery method: Online
Learn more: Program details - Program: B.S. in Computer Information Technology - Cybersecurity Concentration
Credits: 120
Cost per credit: $551
Delivery method: Online
Learn more: Program details - Program: Bachelor of Science in Cybersecurity
Credits: 180
Cost per credit: $420
Delivery method: Campus & online
Learn more: Program details
Cybersecurity master’s degrees in Kentucky
The primary advantage of a master’s degree is that the graduate will not be held back within the company. For instance, some companies may stipulate that those in upper management must have a master’s degree or higher.
Graduates with a master’s degree also, on average, earn a higher salary and have more employment opportunities as their expertise is more in demand.
Kentucky offers four cybersecurity master’s degrees. For more information, please see the list below.
- Program: Master of Science in Cybersecurity Management online
CAE designation: CAE-CD
Credits: 30
Cost per credit: $549
Delivery method: Online
GRE requirement: Required
Learn more: Program details - Program: Master of Science in Cybersecurity Online
CAE designation: CAE-CD
Credits: 30
Cost per credit: $480
Delivery method: Online
GRE requirement: Not required
Learn more: Program details - Program: Master of Science in Information Systems Security
Credits: 30
Cost per credit: $355
Delivery method: Online
GRE Requirement: Not required
Learn more: Program details - Program: Master of Science in Cybersecurity Data Analytics
Credits: 30
Cost per credit: $607 in-state | $917 out of state
Delivery method: Online
GRE requirement: Not required
Learn more: Program details
Cybersecurity certifications in Kentucky
Cyberseek’s data provides insight into the present number of professionals holding prominent cybersecurity certifications in the U.S:
- CompTIA Security+: 265,992 certified
- Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP): 91,765 certified
- Global Information Assurance Certification (GIAC): 46,318 certified
- Certified Information Systems Auditor (CISA): 35,812 certified
- Certified Information Security Manager (CISM): 20,300 certified
- Certified Information Privacy Professional (CIPP): 13,652 certified
Certifications are a complement to a bachelor’s or master’s degree. They train students in a particular cybersecurity skill, and some jobs may require candidates to possess a certain certification as a prerequisite to being hired.
Kentucky has five certification programs. Please consult the following list for more information.
- Program: Cyber Security Certificate
Credits: 12-13
Cost per credits: $255
Delivery method: Online
Learn more: Program details - Program: Cybersecurity Certificate
Credits: 22
Cost per credit: $438 in state | $879 out of state
Delivery method: Campus & online
Learn more: Program details - Program: Digital Forensics Specialist - Certificate
Credits: 20
Cost per credit: $186 in state | $250 out of state
Delivery method: Hybrid
Learn more: Program details - Program: Cybersecurity Certificate
Credits: 32
Cost per credit: $420
Delivery method: Campus & online
Learn more: Program details - Program: Cybersecurity Analytics Graduate Certificate
Credits: 12
Cost per credit: $607 in-state | $917 out of state
Delivery method: Online
Learn more: Program details
Cybersecurity jobs in Kentucky
Recently, there has been an alarming shortage of cybersecurity technicians throughout the United States. The jobs are there, the salaries are above average, but still there are tens of thousands of unfilled vacancies.
A CNN article in 2019 highlighted the problems Kentucky is having securing its voting equipment. While a great deal of that problem is funding-related, also highlighted is the lack of cybersecurity technicians to work with the digital voting equipment.
This is just one small example of the many industries that are understaffed when it comes to cybersecurity. Given this shortage, candidates with a cybersecurity degree have a great deal of choice in which industry they’d like to work.
Government voting, advanced manufacturing, shipping, and logistics, etc. As more industries become digitized, the demand for cybersecurity technicians is only going to grow.
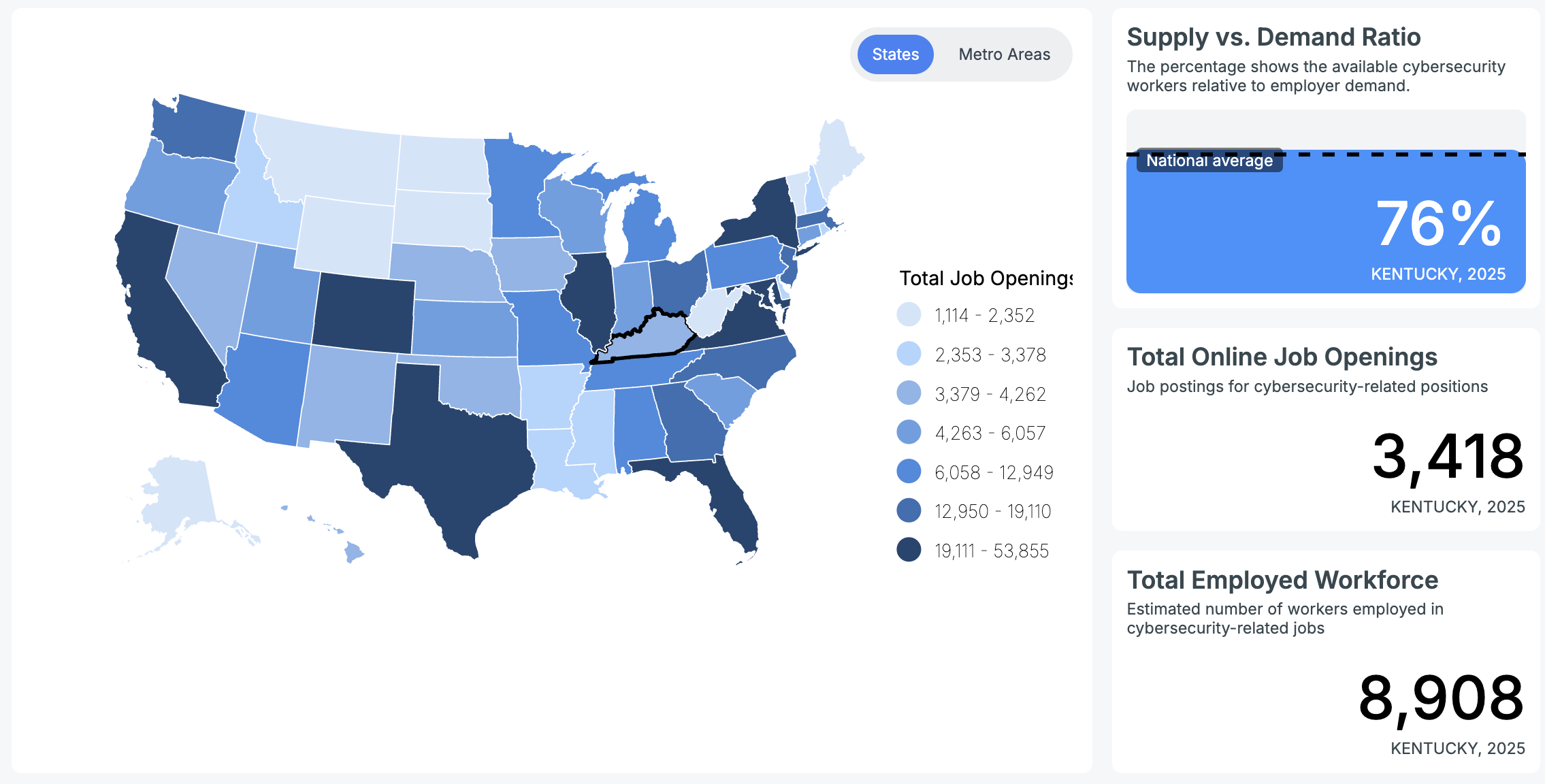
The Bureau of Labor Statistics reported that the average rate of security analysts in Kentucky is $47.22, and the average annual salary of $98,210. Cyberseek website also reported that 8,908 cybersecurity workers are currently employed and there are 3,418 jobs available in Kentucky.
Cybersecurity in Kentucky
Like much of America, Kentucky is becoming increasingly automated. From their advanced manufacturing industry, which employs a not-insignificant amount of the state’s total workers, to their shipping and thriving export economy, everything depends on computers and those computers are susceptible to a cyberattack.
Kentucky’s corporations and government organizations are aware of the threat posed and there is a huge demand for cybersecurity technicians with not enough people to fill the vacancies.
Given the high demand and low supply, there has never been a better time to take an education in cybersecurity. The job market is wide open and the salary is excellent.
Kentucky has a wide variety of cybersecurity education programs, especially undergraduate programs, and getting a degree could be a great way to start a new career in an industry that’s only set to expand.