- Associate degree
- Bachelor’s degree
- Master’s degree
- Cybersecurity certifications
- Cybersecurity in Oklahoma
- Jobs in Oklahoma
This guide is a comprehensive review of the cybersecurity schools in Oklahoma. The guide also covers some of the basic economic factors about the outlook for the cybersecurity industry in the state.
Oklahoma has always relied heavily on agriculture to bolster its economy, particularly ranching. The oil and gas industry has been, by far, the biggest contributor to the state’s economic output for decades, if not in number of people employed. But the economy has diversified in recent decades.
Other large contributors to employment opportunities now include healthcare and education, business and professional services, trade and transportation, and leisure and hospitality.
The government is the single largest employer in Oklahoma, with trade and transportation a close second.
The healthcare industry is, of course, a primary employer of cybersecurity services due to the huge stores of sensitive information that healthcare-related companies collect and store. Business services companies also tend to be prolific employers of cybersecurity professionals.
Ad
cybersecurityguide.org is an advertising-supported site. Clicking in this box will show you programs related to your search from schools that compensate us. This compensation does not influence our school rankings, resource guides, or other information published on this site.
Featured Cybersecurity Degree Programs
| School Name | Program | More Info |
|---|---|---|
| Purdue Global | Online BS in Cybersecurity | website |
| Grand Canyon University | Online BS in Cybersecurity or Online MS in Cybersecurity | website |
| UC Berkeley School of Information | Master’s in Cybersecurity | No GRE/GMAT Required | website |
| Southern New Hampshire University | Online BS in Cybersecurity or Online MS in Cybersecurity | website |
| Arizona State University | Online MA in Global Security - Cybersecurity | website |
Cybersecurity environment in Oklahoma
The state of Oklahoma coordinates its cybersecurity efforts through the Oklahoma Office of Homeland Security.
Oklahoma also participates in the Multi-State Information Sharing and Analysis Center (MS-ISAC), which collects cybersecurity-related data in all 50 states and then distributes that information to participating states so that they can better monitor and prepare for state-level cybersecurity threats.
Related resources
Oklahoma is actively working to strengthen its cybersecurity defenses and to create an environment that supports innovation and education in this field.
Here are some of the key players in Oklahoma’s cybersecurity landscape:
- Oklahoma Cyber Command: This is a division within the Oklahoma Office of Management and Enterprise Services (OMES), specifically focused on protecting the state’s digital resources from cyber threats through proactive threat hunting, incident response, and security monitoring.
- Oklahoma Information Sharing and Analysis Center (OK-ISAC): OK-ISAC serves as a central resource for gathering information on cyber threats to critical infrastructure and providing two-way sharing of information between the private and public sectors.
- Center for Cybersecurity at the University of Tulsa: This center focuses on education and research in cybersecurity. It offers degree programs and is involved in cutting-edge cybersecurity research.
- Oklahoma State University Institute of Technology (OSUIT): OSUIT has programs in Information Technologies with a focus on cybersecurity, preparing students for the growing number of jobs in this field.
- Rose State College Cyber Security Program: Provides cybersecurity educational programs that are recognized by the National Security Agency (NSA) and the Department of Homeland Security (DHS) as a Center of Academic Excellence in Cyber Defense Education.
- Oklahoma National Guard: The Guard has cyber units that not only serve in defense of the nation but can be mobilized to protect the state’s infrastructure against cyber threats.
- InfraGard Oklahoma Members Alliance: This is a partnership between the FBI and the private sector, and the Oklahoma Members Alliance focuses on the sharing of information and intelligence to prevent hostile acts against the U.S.
- The Oklahoma Cyber Alliance (OCA): A collaboration of businesses, educational institutions, and law enforcement, OCA is dedicated to improving the cyber workforce and economic development related to cybersecurity in the state.
- ISSA (Information Systems Security Association) Oklahoma Chapter: The ISSA chapter in Oklahoma provides networking opportunities, professional development, and knowledge sharing for cybersecurity professionals.
- SANS Oklahoma City: SANS provides intensive, immersion training designed to help individuals master the practical steps necessary for defending systems and networks.
Cybersecurity education in Oklahoma
As Oklahoma has a relatively small market for cybersecurity professionals, it isn’t surprising that education programs with information security specialties are fairly limited.
Still, at least one institution, Oklahoma State University, has recognized the need to educate new cybersecurity experts and is taking advantage of the opportunity presented by the growing demand for infosec degrees and certifications.
Oklahoma State University (OSU) hosts an annual cybersecurity conference in Oklahoma City. Way back in 2002, the school established the Center for Telecommunications and Network Security (CTANS) to “serve as the focal point for education and research for information assurance.”
The National Security Administration and the Department of Homeland Security recognize OSU as a Center for Academic Excellence (CAE) in Information Assurance Education and Research. OSU also provides more cybersecurity education options than any other school in Oklahoma.
Cybersecurity associate degree in Oklahoma
Associate’s degrees in cybersecurity are recognized by many employers as adequate education for many entry-level information security positions. Associate’s degrees typically only require one to two years for completion, so they are an excellent alternative for aspiring infosec professionals with constrained resources and/or time.
Many bachelor’s degree programs recognize associate’s degree coursework as credit substitutes for undergraduate classes. So when it comes time to move education to the next level, the time commitment required can be significantly reduced by a previous associate’s degree.
Campus-based associate degrees
- Program: Associate in Applied Science in IT – Information Assurance/Security
Credits: 63-64
Cost per credit: $230 in state | $544 out of state
Delivery method: Campus
Program highlights:- Overview: This program prepares students for IT jobs in businesses, industries, and government.
- What Students Will Learn: Understand IT ethics, create and setup computer software.
- Jobs: Those who complete this program can anticipate successful employment in various positions across business, industry, and government sectors.
- Program: Cyber/Information Security, A.A.S.
CAE designation: CAE-CD
Credits: 61
Cost per credit: $101
Delivery method: Campus
Program highlights:- All-Encompassing Syllabus: From foundational computer skills to in-depth subjects like cyber forensics, the program offers a wide range of topics.
- Practical Experience: Courses such as "Server Management" and "Cloud Computing" provide hands-on learning opportunities.
- Preparation for the Real World: With subjects like "Cyber Forensics," students are equipped to handle actual cybersecurity scenarios.
- Program: Associate in Applied Science in Information Technology – Computer Forensics Option
CAE designation: CAE-R
Credits: 60
Cost per credit: $130 in state | $371 out of state
Delivery method: Campus
Program highlights:- Overview: It teaches students about computers and networking, mainly focusing on Microsoft.
- Job Opportunities: The demand for computer support experts and system managers is growing. Those with current skills and certifications will have better job chances.
- Microsoft Training: OSU-Oklahoma City is a Microsoft Imagine Academy, providing students with the latest IT skills and certification chances.
Cybersecurity bachelor’s degree in Oklahoma
Today’s cybersecurity employers require bachelor’s degrees as a minimum educational background for most information security careers. And the degrees don’t necessarily need to be in cybersecurity. Most technology and science degrees, especially in STEM disciplines, are acceptable.
However, those with a bachelor’s degree in some cybersecurity specialty, or at least with a concentration in cybersecurity, will enjoy a decided advantage when applying for information security positions.
Campus-based bachelor’s degrees
- Program: Bachelor of Science in IT – Information System/Cybersecurity
Credits: 124
Cost per credit: $224 in-state | $538 out-of-state
Delivery method: Campus
Program highlights:- About the Program: A unique aspect of this program is its focus on both tech skills and business communication.
- Specialization: It provides specializations in Computer Systems, Management Systems, and Cyber Security.
- Experience: Graduates are prepared for various IT challenges.
- Program: Bachelor of Science in Cyber Security
Credits: 124
Cost per credit: $260 in-state | $548 out-of-state
Delivery method: Campus
Program highlights:- What the Program Teaches: Understand local and global cyber challenges and know the laws and ethics related to online security.
- Jobs After Graduation: Positions in threat analysis or cyber management and jobs in risk analysis or security testing.
- Other Details: NSU helps students transferring from other schools.
- Program: B.S. Degree in Computer Science with Cybersecurity
CAE designation: CAE-CD
Credits: 126
Cost per credit: $720
Delivery method: Campus
Program highlights:- Program Details: It's designed for students interested in cybersecurity and computer science jobs.
- What You'll Learn: Applying Christian values in computer science and skills for cybersecurity jobs.
- Courses Offered: Advanced topics like Database Systems and Cybersecurity.
- Program: Management Information Systems bachelor’s degree – Information Assurance Major
CAE designation: CAE-R
Credits: 120
Cost per credit: $464 in-state | $981 out-of-state
Delivery method: Campus, Online
Program highlights:- Awards: The program is recognized nationally for excellence in cyber defense education.
- Scholarships: Students in the Spears Business school received $2M in scholarships this year.
- Student Clubs: There's a club where students learn about the latest in information security.
Online bachelor’s degrees
- Program: Management Information Systems bachelor’s degree – Information Assurance Emphasis
CAE designation: CAE-R
Credits: 120
Cost per credits: $464 in-state | $981 out-of-state
Delivery method: Campus, Online
Program highlights:- Recognition: OSU is ranked by CyberDegrees.org for its strong cyber security courses.
- Student Clubs: OSU has a club where students learn about the latest in information security, helping them get ready for jobs after graduation.
- Career Support: The Eastin Center at OSU helps students prepare for their careers.
- Program: Bachelor of Technology in Information Technologies – Cyber Incident Response Option
Credits: 121
Cost per credit: $192 in state | $379 out of state
Delivery method: Online
Program highlights:- About the Program: OSUIT's Cyber Incident Response course trains students to detect and handle cyber threats.
- Job Prospects: After completing the course, students can work in roles like Penetration Tester, Security Manager, and Chief Information Security Officer.
- About OSUIT: OSUIT is known for its top-notch tech education, great teaching facilities, and a 90% job rate for its graduates.
- Program: Bachelor of Technology in Information Technologies – Cybersecurity and Digital Forensics
Credits: 121
Cost per credit: $192 in state | $379 out of state
Delivery method: Online
Program highlights:- What You'll Learn: Students will be trained to protect digital data, handle cybersecurity challenges, investigate online crimes, communicate well, and use best practices in cybersecurity.
- Course Content: The program covers everything from basic programming to advanced security topics.
- Job Prospects: Graduates can aim for roles like Security Analysts and Database Administrators, with salaries ranging from $83,510 to $99,730 annually.
Cybersecurity master’s degree in Oklahoma
As the cybersecurity industry continues to grow and advance, the need for master-level education is also on the rise. Management-level information assurance career paths often now require a master’s degree in cybersecurity.
C-suite corporate posts and careers in academia, cybersecurity research, or cybersecurity consulting most often demand at least graduate-level specialty degrees.
Campus-based master’s degrees
- Program: Master of Science in Computer Science with Cybersecurity
CAE designation: CAE-CD
Credits: 30
Cost per credit: $605
GRE/GMAT Required: Required
Delivery method: Campus
Program highlights:- For Working Individuals: Evening classes make it easy for students to work and study. The university offers guidance from teachers and staff.
- Quick & Flexible: Classes are held one or two nights weekly, lasting eight weeks each. Students can finish the course in about a year, with multiple starting points.
- Practical Learning: The focus is on real-world skills, ensuring students are job-ready.
- Program: Master of Science in Management Information Systems - Emphasis in Cybersecurity
CAE designation: CAE-R
Credits: 34
Cost per credit: $472 in state | $1118 out of state
GRE/GMAT Required: Required
Delivery method: Campus
Program highlights:- Program Aim: The course focuses on solving tech and security issues in businesses.
- Faculty: The teachers are well-known experts who are involved in current research.
- Fees & Support: Costs depend on factors like scholarships and the number of courses taken. Some students can get assistantships to help with costs.
Online master’s degree programs
- Program: Master of Science in Cyber Security
CAE designation: CAE-CD, CAE-R
Credits: 30
Cost per credit: $1,431
GRE/GMAT Required: Required
Delivery method: Online
Program highlights:- About the Program: This online Master's program in cyber security is tailored for professionals wanting to boost their cyber skills.
- Courses: It teaches both theory and hands-on techniques to protect digital spaces.
- Jobs: Graduates are ready for jobs in government, law enforcement, and private companies.
Cybersecurity certifications in Oklahoma
Whether a student is looking to get started in cybersecurity or a veteran professional desires further education, there are certifications available for most situations, career needs, and educational desires.
Introductory certifications, cybersecurity specialization certifications, and advanced degree certifications can now be found to suit most career-minded information assurance professionals.
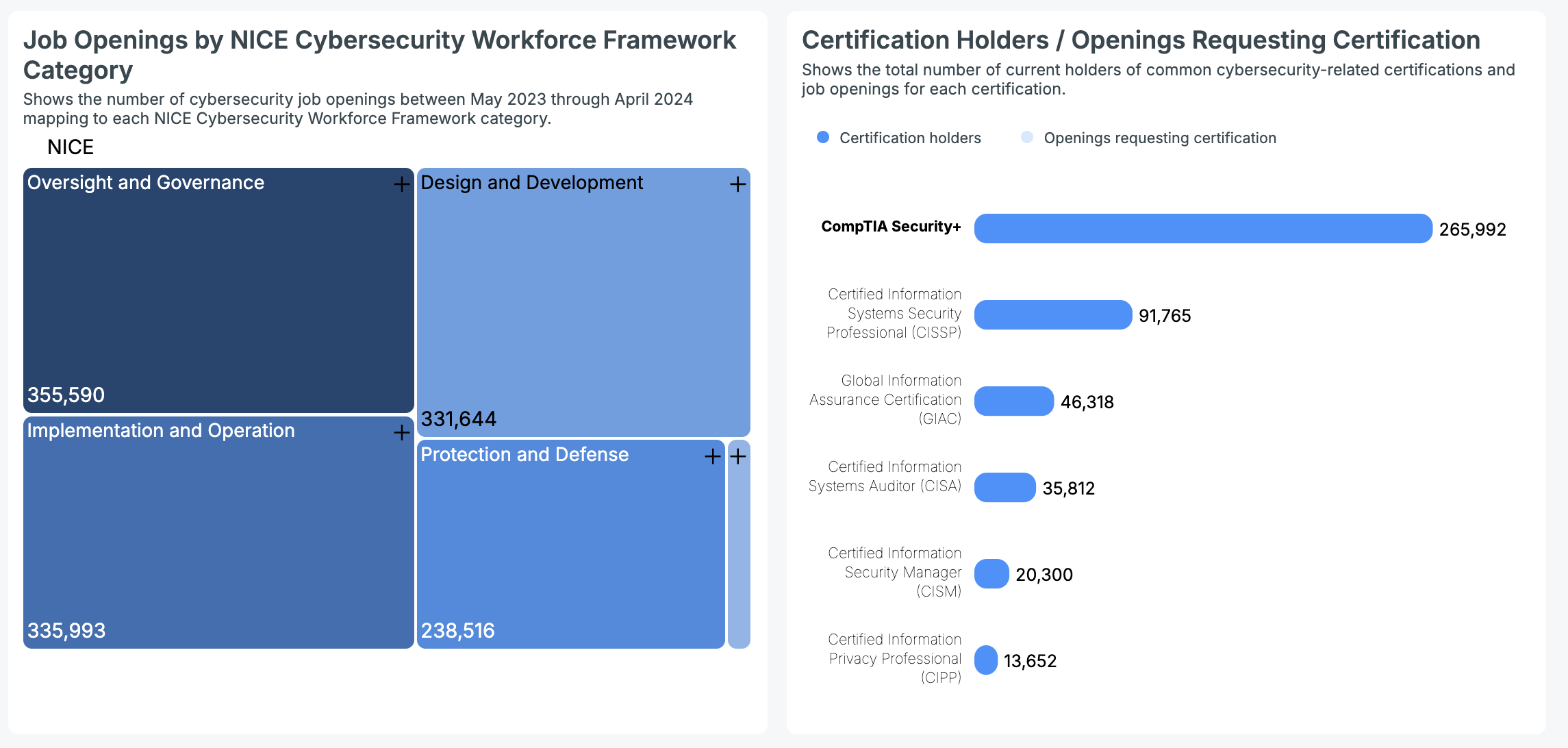
Based on Cyberseek’s comprehensive nationwide data, the current number of professionals holding common cybersecurity certifications is as follows:
- CompTIA Security+: 265,992 certified professionals
- CISSP: 91,765 certified professionals
- GIAC: 46,318 certified professionals
- CISA: 35,812 certified professionals
- CISM: 20,300 certified professionals
- CIPP: 13,652 certified professionals
At present, only Oklahoma City Community College (Certificate of Mastery in Information Security) and Rose State College (Information Security Certificate Program) offer cybersecurity certification programs through campus-based courses.
- Program: Cyber/Information Security, Certificate
CAE designation: CAE-CD
Credits: 45
Cost per credit: $101
Delivery method: Campus
Program highlights:- Overview: This program equips students with a robust understanding of each topic, preparing them for cybersecurity roles.
- Courses: Cyber Forensics: Techniques for probing into cyber-related offenses and security breaches.
- Term of Study: The program is structured over eight terms, with each term focusing on specific areas of computer science and cybersecurity.
- Program: Graduate Certificate in Information Assurance
CAE designation: CAE-R
Credits: 12
Cost per credit: $239 in state | $364 out of state
Delivery method: Online
Program highlights:- Overview: This program dives deep into topics like cyber security and how to protect business data.
- Study: This certificate can also lead to a Master's degree in Management Information Systems with a focus on cybersecurity.
- Focus: The focus of the courses is on providing solutions to business information systems, data, and security needs.
- Program: Cyber Essentials Certificate
CAE designation: CAE-CD
Credits: 18
Cost per credit: $126 in state | $339 out of state
Delivery method: Online
Program highlights:- Program: Designed for students to complete and then enter the workforce.
- About the Certification: They can either be part of the degree plan (embedded certificates) or can be completed as stand-alone certificates.
- Program: Cyber Security Certificate
CAE designation: CAE-CD
Credits: 45
Cost per credit: $126 in state | $339 out of state
Delivery method: Online
Program highlights:- What You'll Learn: Cyber Security: Protecting digital information.
- Purpose: Designed for students who want to directly enter the workforce after completion.
Cybersecurity jobs in Oklahoma
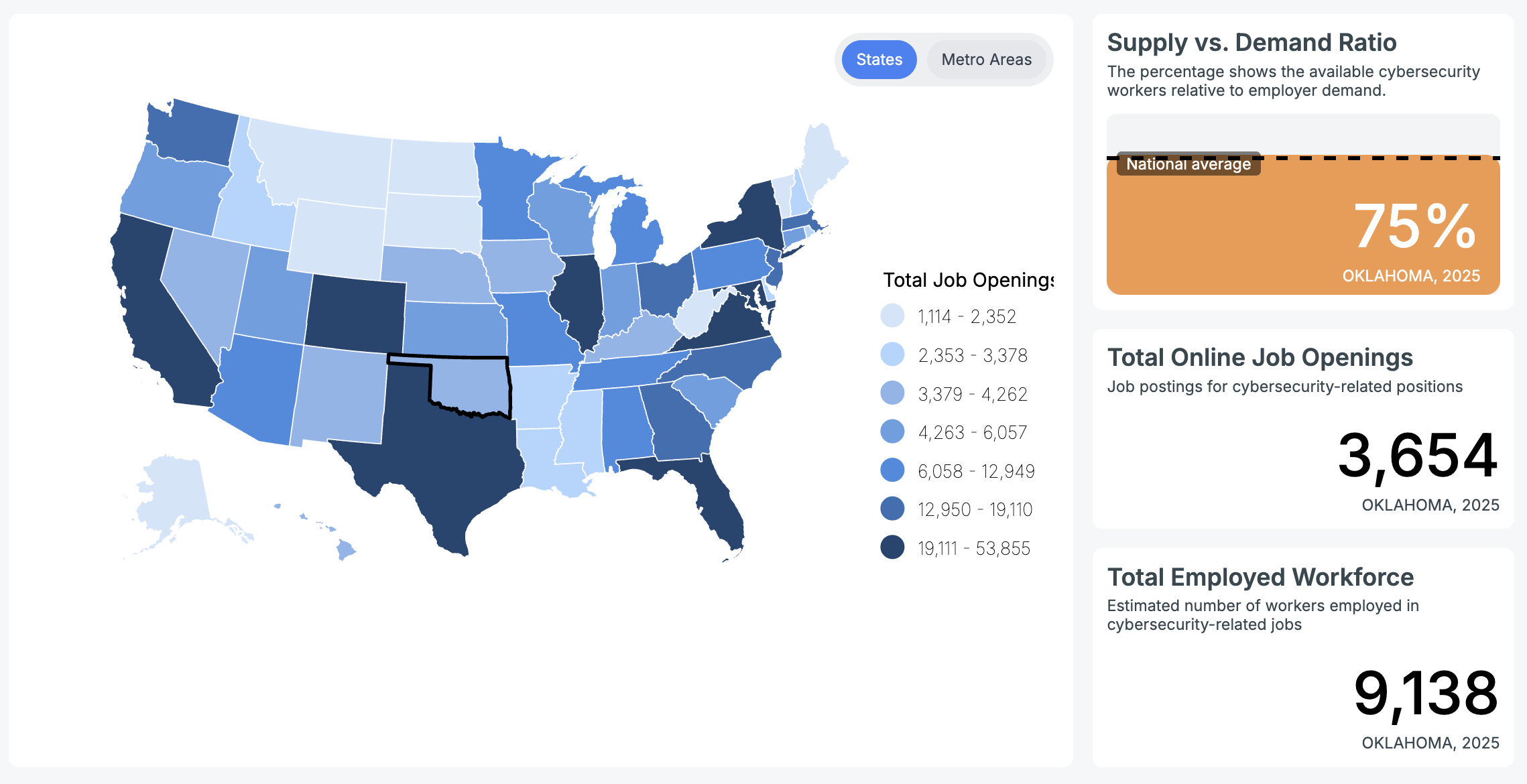
Looking at the cybersecurity jobs in the U.S. between May 2023 and April 2024, there was plenty of action. Oversight and Governance roles were the clear frontrunners with 355,590 openings.
Implementation and Operation (335,993) and Design and Development (331,644) also offered a ton of opportunities. Protection and Defense saw 238,516 roles, and Investigation had 19,525 nationwide.
Oklahoma currently is among the country’s smaller markets for cybersecurity professionals. Cyberseek reported that 9,138 cybersecurity professionals were employed in Oklahoma.
Over that same period, some 3,654 new information security job openings were posted by Oklahoma employers. Oklahoma City (2,573) and Tulsa (662) were easily the most active regions for cybersecurity job openings.
Security analysts, a representative career path in cybersecurity, were receiving relatively low compensation (average hourly wage: $41.59; average annual salary: $86,500), according to the Bureau of Labor Statistics.
Cybersecurity in Oklahoma
The density of cybersecurity professionals as compared to state citizens as a whole is among the lowest in the nation.
While the average time between cybersecurity job postings and candidates chosen is also among the lowest in the US, it is still higher than nearly every other job category is experiencing around the globe.
So while Oklahoma is not the most attractive state in the US for cybersecurity professionals, demand is growing and relatively light competition for job openings should mean applicants have little trouble finding quality career opportunities.