- Associate degree
- Bachelor’s degree
- Master’s degree
- Cybersecurity certifications
- Cybersecurity in Georgia
- Jobs in Georgia
This guide provides an overview of cybersecurity in the state of Georgia. The information below is a summary of cybersecurity educational and career opportunities that now exist in Georgia.
It also includes a review of economic conditions, particularly as it relates to the expected future growth of demand for Georgia cybersecurity services.
Ad
cybersecurityguide.org is an advertising-supported site. Clicking in this box will show you programs related to your search from schools that compensate us. This compensation does not influence our school rankings, resource guides, or other information published on this site.
Featured Cybersecurity Degree Programs
| School Name | Program | More Info |
|---|---|---|
| Keiser University | Online BS in Cybersecurity | website |
| Purdue Global | Online BS in Cybersecurity | website |
| Grand Canyon University | Online BS in Cybersecurity or Online MS in Cybersecurity | website |
| University of West Florida | Online MS in Cybersecurity | website |
| Southern New Hampshire University | Online BS in Cybersecurity or Online MS in Cybersecurity | website |
Georgia ranks 24 by geographic area but eight in terms of largest by population. About 60 percent of the state’s residents live in the Atlanta metropolitan area.
For the past few decades, the Atlanta region has provided most of the economic growth that has taken place in Georgia. Industries such as financial services and technology took root in the 1970s and 1980s and are now mainstays for the state’s economy.
In the past year, the state of Georgia has experienced strong demand for cybersecurity professionals. In terms of new cybersecurity job openings, Georgia ranked eighth in the country behind North Carolina.
Georgia is home to 17 Fortune 500 corporations, including Home Depot, Coca-Cola, Delta Air Lines, UPS, SunTrust Banks, Anthem, and Honeywell.
Aside from the large financial services industry, the state government has thrown its support behind developing the cybersecurity industry, in addition to fortifying the state’s information security readiness.
Growing importance of cybersecurity in Georgia
The state government created the Georgia Technology Authority (GTA) “way back” in the year 2000. It was one of the first state-sponsored cybersecurity organizations established in the US. One of GTA’s missions is to ensure the security of the state’s information technology infrastructure.
Then in January 2017, the governor announced the creation of the Georgia Cyber Center in Augusta, subsequently building a $100 million facility to house the Center. Its two-fold mission is to educate the next generation of cybersecurity professionals and to support innovative cybersecurity companies based within the state.
In 2017, the US Department of Homeland Security (DHS) completed a case study of how the state of Georgia has organized and executed its efforts to maximize cybersecurity in the state. The study was used as an example of successful cyber governance for other states to follow.
In 2018, the GTA initiated the Cybersecurity Workforce Academy within the Georgia Cyber Center to educate cybersecurity professionals working in state agencies.
The Academy and the Center now collaborate to offer cybersecurity certificate programs and are also involved with several undergraduate and graduate cybersecurity education programs.
In 2020, Fort Gordon in Augusta became the national U.S. Army Cyber Command central post for all of the U.S. Army’s Cybersecurity Operations. The plan calls for more than 4,700 high-tech military personnel to be relocated to Georgia.
The Command center will include a “cyber range” to provide real-world cyber warfare training and technology research. In addition to enhancing the nation’s information security, the state intends to use it to help train young students showing an interest in cybersecurity.
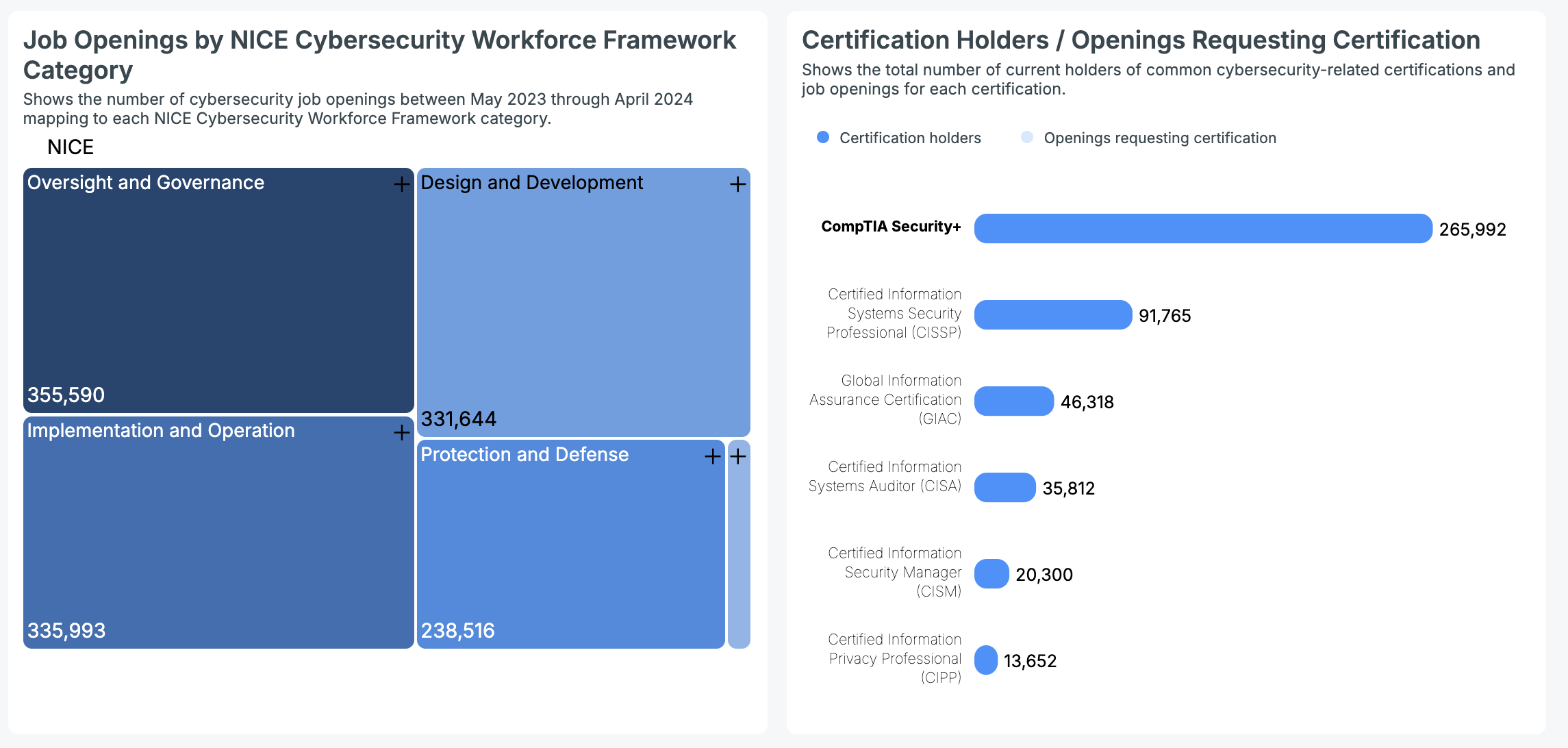
Between May 2023 and April 2024, U.S cybersecurity job openings, as categorized by the NICE Cybersecurity Workforce Framework, included: Oversight and Governance (355,590), Implementation and Operation (335,993), Protection and Defense (238,516), Design and Development (331,644), and Investigation (19,525).
Like everywhere, Georgia’s economic strength will be largely dependent upon the state’s ability to educate and attract cybersecurity professionals in the future. The government and business community are already acutely aware of what needs to be done.
Unlike many other states, Georgia is taking the challenge seriously, which should make it a hospitable place for the cybersecurity industry to thrive.
Related resources
Cybersecurity education in Georgia
With support from the state government, Georgia’s colleges and universities are taking their role in cybersecurity efforts seriously, particularly the state university system.
There are already eight schools that have been awarded the NSA’s designation for Centers of Academic Excellence in Cyber Defense (CAE-CD), including Augusta University, Columbus State University, Georgia Institute of Technology (Georgia Tech), Georgia Southern University, Kennesaw State University, the University of Georgia, and the University of North Georgia.
Georgia Tech has developed a Cyber and Network Security Boot Camp for information security beginners. The intent is to produce students knowledgeable in many different aspects of cybersecurity.
The University of Georgia created the Institute for Cybersecurity and Privacy (ICSP) in Athens, Georgia. ICSP’s mission is to be “a state hub for cybersecurity research and education.” The NSA has designated the institute as a CAE in Cybersecurity Research.
In 2004, Kennesaw State was the first US educational institution to be recognized by the NSA as a CAE and has continued to hold various CAE designations ever since. The school’s Institute for Cybersecurity Workforce Development was founded to oversee the school’s cybersecurity education programs and to work with state authorities to assist in public information security efforts.
Given the state’s determination to be a leading influencer in cybersecurity and the resources being brought to bear by the state university system, there are likely few states better suited to provide a quality education, learning environment, and post-graduation career opportunities than Georgia.
This is particularly true for undergraduate degrees. Bachelor’s degree and certificate programs are plentiful in Georgia. At present, though, there is a lack of associate’s and Ph.D. programs, but that is likely to change in the coming years.
Cybersecurity associate degrees in Georgia
Associate’s degrees in cybersecurity generally require only a year or two to complete, so they provide a good alternative to bachelor’s degrees for those lacking the time and resources to complete a four-year program.
- Program: Cybersecurity AAS
Credits: 72
Cost per credit: $153
Delivery Method: Campus, Online
Learn more: Program details - Program: Cybersecurity, Associate of Applied Science Degree
CAE designation: CAE-CD
Credits: 72
Cost per credit: $531
Delivery Method: Campus
Learn more: Program details - Program: Cybersecurity Associate of Applied Science Degree
Credits: 70-72
Cost per credit: $100 in state | $200 out of state
Delivery Method: Campus
Learn more: Program details - Program: AS in Cyber Security
Credits: 65-69
Cost per credit: $226
Delivery Method: Campus, Online
Learn more: Program details - Program: Cybersecurity Associate Degree
Credits: 65-69
Cost per credit: $148 (Campus) | $169 (Online)
Delivery Method: Campus, Online
Learn more: Program details - Program: Cybersecurity (IS23) Associate of Applied Science Degree
Credits: 72
Cost per credit: $100 in state | $200 out of state
Delivery Method: Campus, Online
Learn more: Program details - Program: Associate in Applied Science in Cybersecurity
Credits: 60
Cost per credit: $100 in state | $400 out of state
Delivery Method: Campus
Learn more: Program details - Program: Cybersecurity, AAS
CAE designation: CAE-CD
Credits: 72
Cost per credit: $100 in state | $400 out of state
Delivery Method: Campus
Learn more: Program details - Program: Cybersecurity associate degree
Credits: 72
Cost per credit: $100
Delivery Method: Campus, Online
Learn more: Program details
Cybersecurity bachelor’s degrees in Georgia
While some cybersecurity employers require only an associate’s degree for entry-level job openings, most information security positions now call for at least a bachelor’s degree.
Often, employers will require a technology major, preferably in a STEM-based discipline. However, majoring or having a concentration in cybersecurity will certainly be viewed favorably over other technology majors.
Campus-based bachelor’s degree
- Program: Cybersecurity Degree
Credits: 72
Cost per credit: $100
Delivery Method: Campus
Learn more: Program details - Program: Cyber Security Minor
Credits: 124 (18 Cybersecurity Credits)
Cost per credit: $182 in-state | $643 out-of-state
Delivery Method: Campus
Learn more: Program details - Program: Cybersecurity Minor
CAE designation: CAE-CD
Credits: 120 (16 cybersecurity)
Cost per credit: $187 in-state | $658 out-of-state
Delivery Method: Campus
Learn more: Program details
Online bachelor’s degree
- Program: Bachelor of Science in Cybersecurity
CAE designation: CAE-CD
Credits: 120
Cost per credit: $185 in state | $654 out of state
Delivery Method: Online
Learn more: Program details
Cybersecurity master’s degrees in Georgia
Master’s degrees in cybersecurity are growing in importance in the industry. Management-level information security jobs are increasingly demanding applicants have a graduate degree in a cybersecurity specialty.
C-suite corporate positions like Chief Information Security Officer almost always now require a master’s degree, and sometimes even a PhD.
Also, cybersecurity professionals choosing to pursue a career in academia, cybersecurity research, or cybersecurity consulting are now finding master’s degrees beneficial for landing quality positions.
- Program: Master’s of Science in Cybersecurity
CAE designation: CAE-R
Credits: 32
Cost per credit: $310
Delivery Method: Online
GRE/GMAT Required: Not Required
Learn more: Program details - Program: Master of Science in Cybersecurity
CAE designation: CAE-CD
Credits: 30
Cost per credit: $296 in-state | $1,066 out of state
Delivery Method: Online
GRE/GMAT Required: Not Required
Learn more: Program details
Cybersecurity certifications in Georgia
Cybersecurity certifications are perfect vehicles for students just starting in cybersecurity and for experienced professionals. A range of various types of certification programs is available depending on individual circumstances and needs.
- Program: Cybersecurity Certificate
Credits: 26
Cost per credit: $159
Delivery Method: Campus
Learn more: Program details - Program: Cyber Security Certificate
Credits: 26
Cost per credit: $100 in state | $200 out of state
Delivery Method: Campus
Learn more: Program details - Program: Cybersecurity (IS81) Certificate
Credits: 26
Cost per credit: $100 in state | $200 out of state
Delivery Method: Campus
Learn more: Program details - Program: Cybersecurity Certificate
Credits: 34
Cost per credit: $100 in state | $200 out of state
Delivery Method: Campus
Learn more: Program details - Program: Cybersecurity Certificate
Credits: 26
Cost per credit: $100
Delivery Method: Campus
Learn more: Program details - Program: Cybersecurity Certificate - Technical Certificate of Credit
Credits: 26
Cost per credit: $100 in state | $200 out of state
Delivery Method: Campus
Learn more: Program details - Program: Graduate Certificate in Cybersecurity
CAE designation: CAE-R
Credits: 18-20
Cost per credit: $370 in-state | $1,050 out of state
Delivery Method: Campus
Learn more: Program details - Program: Cybersecurity certificate
Credits: 26
Cost per credit: $100 in-state | $200 out of state
Delivery Method: Campus, Online
Learn more: Program details
Here’s the information on the total number of current holders of common cybersecurity-related certifications in the U.S:
- CompTIA Security+: 265,992 certification holders
- CISSP): 91,765 certification holders
- GIAC): 46,318 certification holders
- CISA): 35,812 certification holders
- CISM: 20,300 certification holders
- CIPP: 13,652 certification holders
Trying to decide if cybersecurity is the right career? Try a certification program designed to provide an introduction to information security.
When it comes time to apply for entry-level positions in cybersecurity, these certifications will prove to be an advantage.
Cybersecurity bootcamps in Georgia
- Program: Cybersecurity Certificate Bootcamp
Credits: 15-30 weeks
Cost per credit: $9,500
Delivery Method: Online
Learn more: Program details - Program: Cybersecurity Boot Camp
CAE designation: CAE-CD
Credits: 6 months
Cost per credit: $4,275
Delivery Method: Online
Learn more: Program details - Program: Cybersecurity Master Boot Camp
Credits: 6 months
Cost per credit: $4,275.00
Delivery Method: Online
Learn more: Program details
Cybersecurity jobs in Georgia
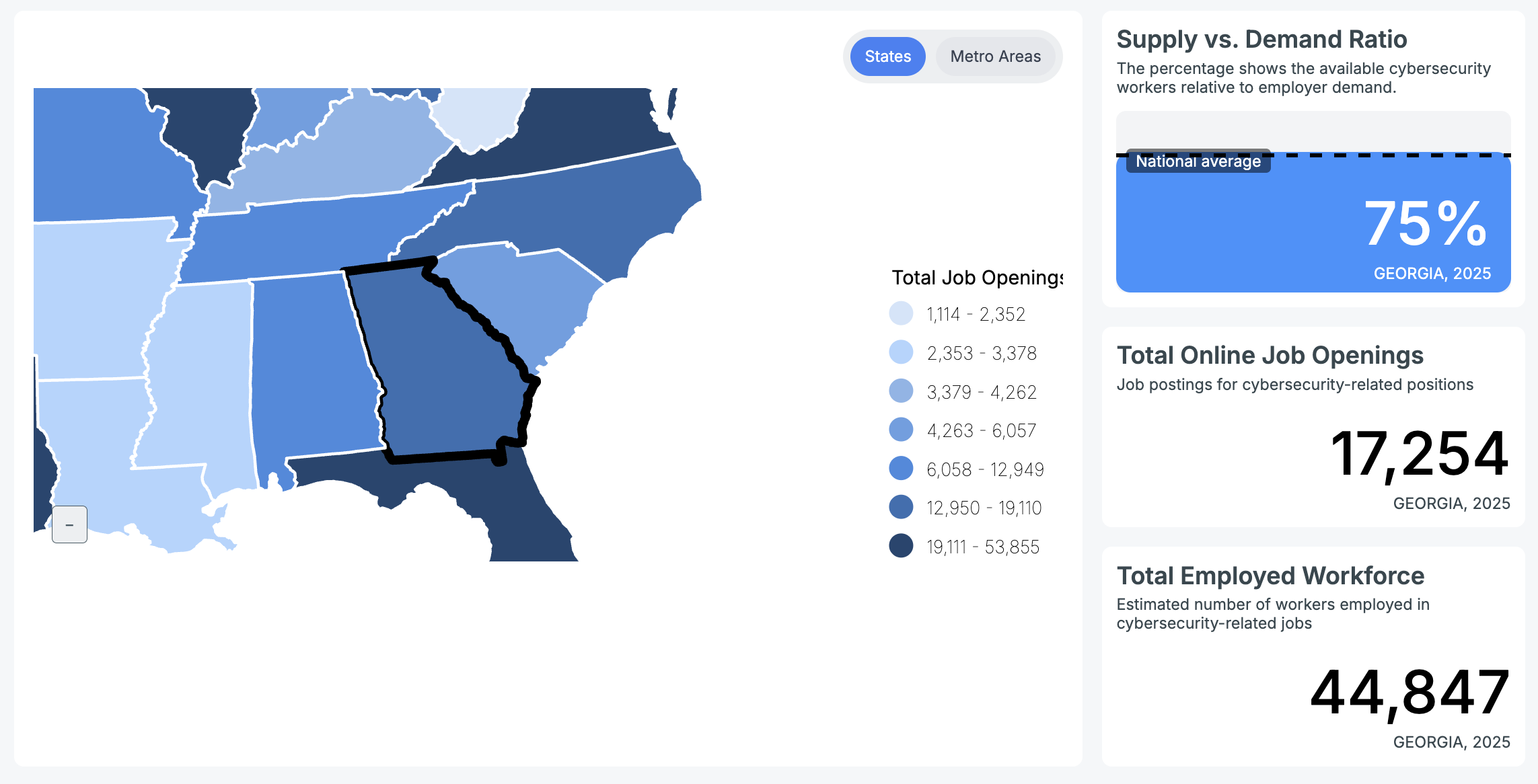
CyberSeek reports that there were 44,847 cybersecurity professionals employed in the state of Georgia. There were also 17,254 new information security jobs posted by Georgia employers during that time.
Compared to other states in the US, Georgia has a very high concentration of cybersecurity job demand.
There are more than 120 cybersecurity companies based in the state of Georgia, including IBM Security Services, generating nearly $5 billion in annual revenues.
Cybersecurity jobs in the Atlanta metropolitan area are by far the biggest contributor to the demand, with 13,544 openings in 2024. The next closest region in Georgia (Augusta) experienced fewer than 736 cybersecurity job openings.
According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, security analysts in Georgia have an average annual salary of $124,270 or $59.75 hourly wage. This is about in line with or slightly lower than national averages. But Georgia also sports a standard of living about seven percent below the national average.
Housing is the biggest reason for the lower cost of living, but most other things tend to be relatively inexpensive in Georgia, too. And even in the Atlanta area, housing is substantially cheaper than the US average.
Cybersecurity in Georgia
Georgia is already one of the leading states in the country for cybersecurity, and everything is being done to ensure that it continues to hold a leadership role. The existing cybersecurity industry is one of the largest in the country and is growing rapidly.
The US Army also opened its cybersecurity central command in Augusta in 2020.
The state government and educational institutions have thrown their full support into ensuring Georgia has a strong supply of new cybersecurity professionals. And a growing economic base has a critical need for infosec services.
With these advantages, Georgia promises to be a prime location for up-and-coming cybersecurity professionals for the foreseeable future.