- Associate degree
- Bachelor’s degree
- Master’s degree
- Cybersecurity certifications
- Cybersecurity in Mississippi
- Jobs in Mississippi
This guide contains a brief insight into cybersecurity education and career opportunities in Mississippi.
Mississippi’s economy shifted from agriculture to manufacturing over the 20th century, converting traditional cotton production to reforestation programs. Poultry provides the primary source of livestock alongside soybeans as its main crop, accounting for the majority of the state’s production value.
Mississippi’s manufacturing sector, which produces automotive parts, lumber, and processed foods, has become a reliable but slowly shrinking source of jobs and income due to industrial development programs.
In contrast, the hospitality and service industry, which includes federal, retail, wholesale, real estate, and social services, remains the state’s primary source of income.
The state government is a major employer, funded primarily by sales taxes. Local governments rely on real estate taxes for revenue, and large employers offer union benefits to boost productivity.
While the transportation sector has declined, it still accounts for 21 percent of employment in the state.
Ad
cybersecurityguide.org is an advertising-supported site. Clicking in this box will show you programs related to your search from schools that compensate us. This compensation does not influence our school rankings, resource guides, or other information published on this site.
Featured Cybersecurity Degree Programs
| School Name | Program | More Info |
|---|---|---|
| Purdue Global | Online BS in Cybersecurity | website |
| UC Berkeley School of Information | Master’s in Cybersecurity | No GRE/GMAT Required | website |
| Grand Canyon University | Online BS in Cybersecurity or Online MS in Cybersecurity | website |
| Arizona State University | Online MA in Global Security - Cybersecurity | website |
| Southern New Hampshire University | Online BS in Cybersecurity or Online MS in Cybersecurity | website |
Related resources
Mississippi is a particularly attractive target for cybercriminals for many reasons. First, the state has a relatively small population and economy. This makes it easier for cybercriminals to blend in and operate undetected.
Second, Mississippi’s economy is heavily reliant on agriculture and other industries that are heavily dependent on technology. These industries are often targeted by cybercriminals who are looking to steal intellectual property or disrupt operations.
In 2017, the legislature enacted the Enterprise Security Program, which requires state agencies to implement cybersecurity measures.
The Mississippi government is also taking steps to address the cybersecurity threat and the state created a cybersecurity unit within the Department of Public Safety.
However, there is still much more that can be done to improve cybersecurity in Mississippi.
Growing awareness of cybersecurity in Mississippi
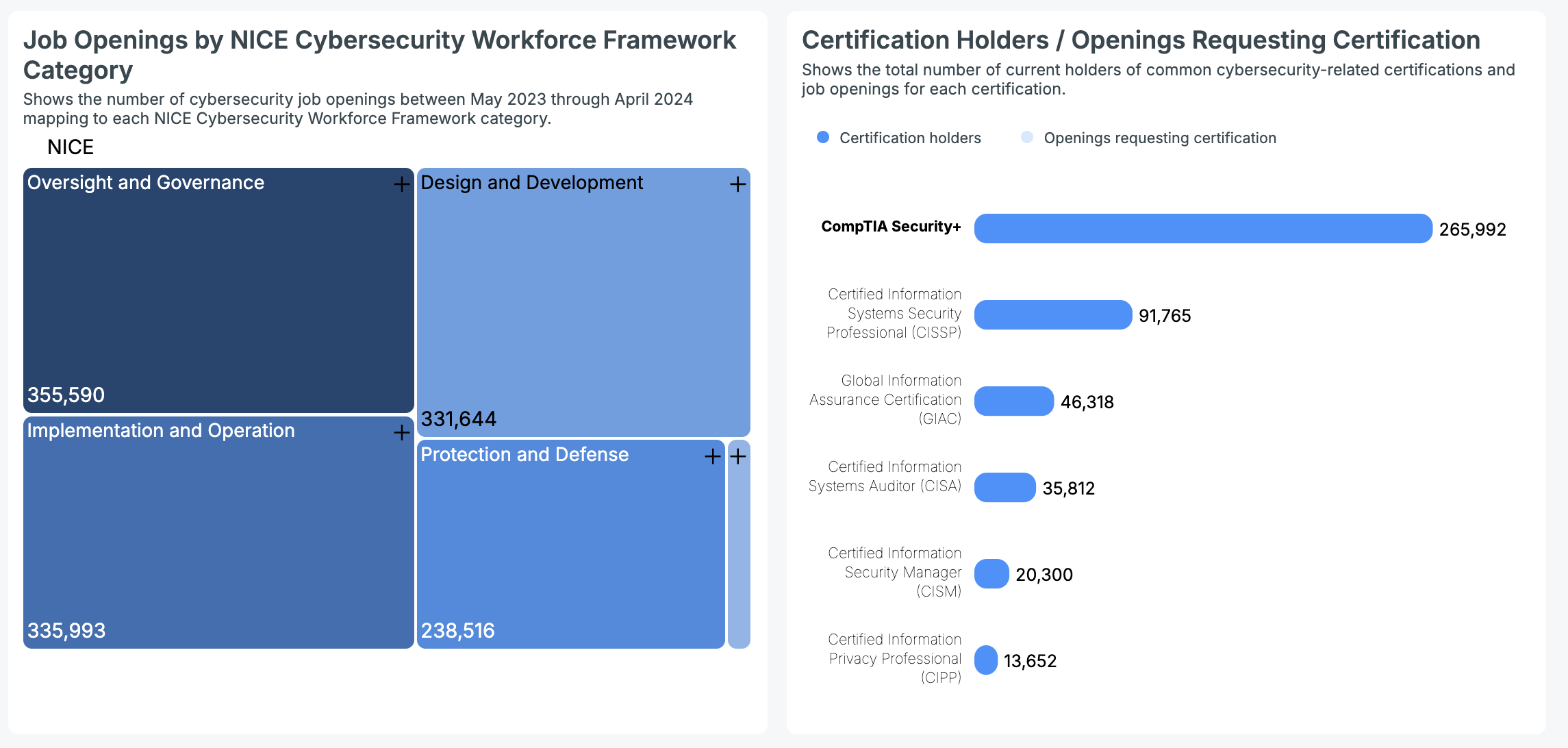
The cybersecurity sector saw significant nationwide demand, with Oversight and Governance leading in job openings (355,590). Implementation and Operation followed with 335,993 positions, and Design and Development had 331,644. Protection and Defense roles accounted for 238,516 openings, while Investigation had 19,525.
According to Mississippi’s Department of Information Technology Services, during the 2017 Legislative session, Mississippi’s legislature enacted the Enterprise Security Program, which supports cybersecurity approaches to state enterprises.
The program outlines overseeing all state agencies to install security programs, systems, services, and policies to acquire technology solutions and assist in new cybersecurity initiatives.
Before this development, the state had only the Enterprise Security Policy, which outlined minimum requirements for agencies to protect data and information technology back in 2013.
Mississippi has established multiple ways to raise awareness of cybersecurity and provide resources for protection in response to the growing threat of cyberattacks against public sector organizations. The state’s Enterprise Cloud and Offsite Hosting Security Policy, which was last updated in 2018, outlines additional requirements for these services.
The Enterprise Security Awareness Training Standard and Cybersecurity Incident Notification Response Standard, both updated in 2019, provide computer-based training and incident response procedures for cybersecurity events.
Among its policies, the Mississippi Statewide Architecture & Technology Infrastructure Plan frames more detailed initiatives and principles to oversee and implement across the state, giving businesses guidance for technology investments and decision-making processes.
Mississippi also holds its annual Cybersecurity Summit to educate citizens about threats, discuss future initiatives, and celebrate advancements during National Cybersecurity Awareness Month, observed every October.
Other cybersecurity organizations in Mississippi:
- Mississippi Department of Information Technology Services (ITS): Responsible for providing IT services and support to state agencies and institutions. It plays a key role in ensuring the cybersecurity of the state’s digital infrastructure.
- Mississippi Office of Homeland Security: Works to safeguard the state from various threats, including cyber threats. It collaborates with other agencies and organizations to enhance cybersecurity preparedness.
- Mississippi State University – Center for Cyber Innovation: Focuses on research and development in cybersecurity. It also offers educational programs to prepare students for careers in cyber defense.
- Mississippi Cybersecurity Education Workforce Initiative (MS-CEWI): The initiative is aimed at addressing the shortage of cybersecurity professionals in the state. It works to enhance cybersecurity education and training.
- Mississippi National Guard – Cyber Protection Team: Works to defend against and respond to cyber threats affecting the state and nation.
- Mississippi Cyber Initiative (MCI): MCI is a non-profit organization that is dedicated to promoting cybersecurity education and awareness in Mississippi. MCI offers a variety of programs and resources, including cybersecurity training, workshops, and conferences.
Cybersecurity education in Mississippi
Mississippi provides its citizens with various academic degree opportunities to increase training and preparation for future information technology careers.
State and local governments require workers handling sensitive data information related to public and private sector companies to have training in computer security methods.
With a cybersecurity degree, those requirements will be met according to current standards, and allow those receptive to gain better employment.
Cybersecurity associate degrees in Mississippi
Traditionally, associate degrees help students prepare for a career in cybersecurity with the necessary concepts. Over two years, students in cybersecurity associate degree programs will train students to handle firewall breaches, secure computer software hacks, and encode sensitive data.
- Program: Cybersecurity Technology Program
Credits: 67
Cost per credit: $146
Delivery method: Campus
Learn more: Program details - Program: Cybersecurity & Networking Technology Program
Credits: 67
Cost per credit: $146
Delivery method: Campus
Learn more: Program details - Program: Associate of Applied Science degree in Computer Networking Technology
Credits: 65
Cost per credit: $165 in state | $265 out of state
Delivery method: Campus
Learn more: Program details - Program: Associate of Applied Science in Cybersecurity Technology
CAE designation: CAE-CD
Credits: 62
Cost per credit: $148 in state | $275 out of state
Delivery method: Campus & online
Learn more: Program details - Program: Associate of Applied Science Degree in Cybersecurity Technology
CAE designation: CAE-CD
Credits: 76
Cost per credit: $165
Delivery method: Campus
Learn more: Program details
Cybersecurity bachelor’s degrees in Mississippi
Bachelor’s degrees typically teach students advanced cybersecurity methods for cloud networking, hardware/software systems, and encryption. This allows students to deepen their knowledge of information security, with flexible terms for course completion and a solid foundation for career advancement.
The University of Southern Mississippi offers an Information Security minor that complements bachelor’s degrees with a focus on network security, IT policies, intrusion detection, Linux administration, and multi-layered network operations.
- Program: Cybersecurity BAS
Credits: 120
Cost per credit: $385 in-state | $469 out-of-state
Delivery method: Online
Learn more: Program details
Cybersecurity master’s degrees in Mississippi
Mississippi College’s MS in Cybersecurity and Information Assurance focuses on cybersecurity leadership and management, with research in analysis and engineering, programming, and design.
Mississippi State University’s MS in Cyber Security and Operations offers advanced, on-campus education for students with software development, hardware and software applications, and data communications skills with mathematical fluency.
- Program: Master of Science in Cyber Security and Information Assurance
Credits: 30
Cost per credit: $713
Delivery method: Campus & online
GRE requirement: Not required
Learn more: Program details - Program: M.S. in Cyber Security and Operations
CAE designation: CAE-CD, CAE-R, CAE-CO
Credits: 31
Cost per credit: $597 in-state | $892 out of state
Delivery method: Campus & online
GRE requirement: Optional
Learn more: Program details
Cybersecurity PhD degrees in Mississippi
Mississippi State University incorporates a full, complete education in cybersecurity and computer science through its Direct Admit Ph.D. program.
The program extends knowledge through specialization, allowing students to research in-depth concepts related to algorithms, computer theories, and the sequential complexity of data composition.
- Program: Ph.D. Computer Science – Computer Security Concentration
CAE designation: CAE-CD, CAE-R, CAE-CO
Credits: 63
Cost per credit: $537
Delivery method: Campus & online
GRE requirement: Not required
Learn more: Program details
Cybersecurity certifications in Mississippi
Cybersecurity certifications are in high demand across the U.S., and Mississippi is no exception. According to Cyberseek’s nationwide data, here are the current numbers for professionals holding common cybersecurity certifications:
- CompTIA Security+: 265,992 certification holders
- CISSP: 91,765 certification holders
- GIAC: 46,318 certification holders
- CISA: 35,812 certification holders
- CISM: 20,300 certification holders
- CIPP: 13,652 certification holders
Here are some Mississippi schools offering programs to help you join their ranks:
- Program: Career Certificate in Cybersecurity
CAE designation: CAE-CD
Credits: 30
Cost per credit: $118 in state | $220 out of state
Delivery method: Campus & onlilne
Learn more: Program details - Program: Graduate Certificate in Cybersecurity & Information Assurance
Credits: 18
Cost per credit: $713
Delivery method: Campus & online
Learn more: Program details - Program: Cybersecurity Technology Certificate
Credits: 32
Cost per credit: $165
Delivery method: Campus
Learn more: Program details
Cybersecurity jobs in Mississippi
Initiatives through the state’s legislature and advancements in cybersecurity education throughout universities grant those committed to cybersecurity careers with potential advantages for jobs.
The continuous shift from agriculture to manufacturing and the tightening grasp on the state’s services and transportation industries lead many in cybersecurity to not only further develop needed services but grow the state’s economic success as well.
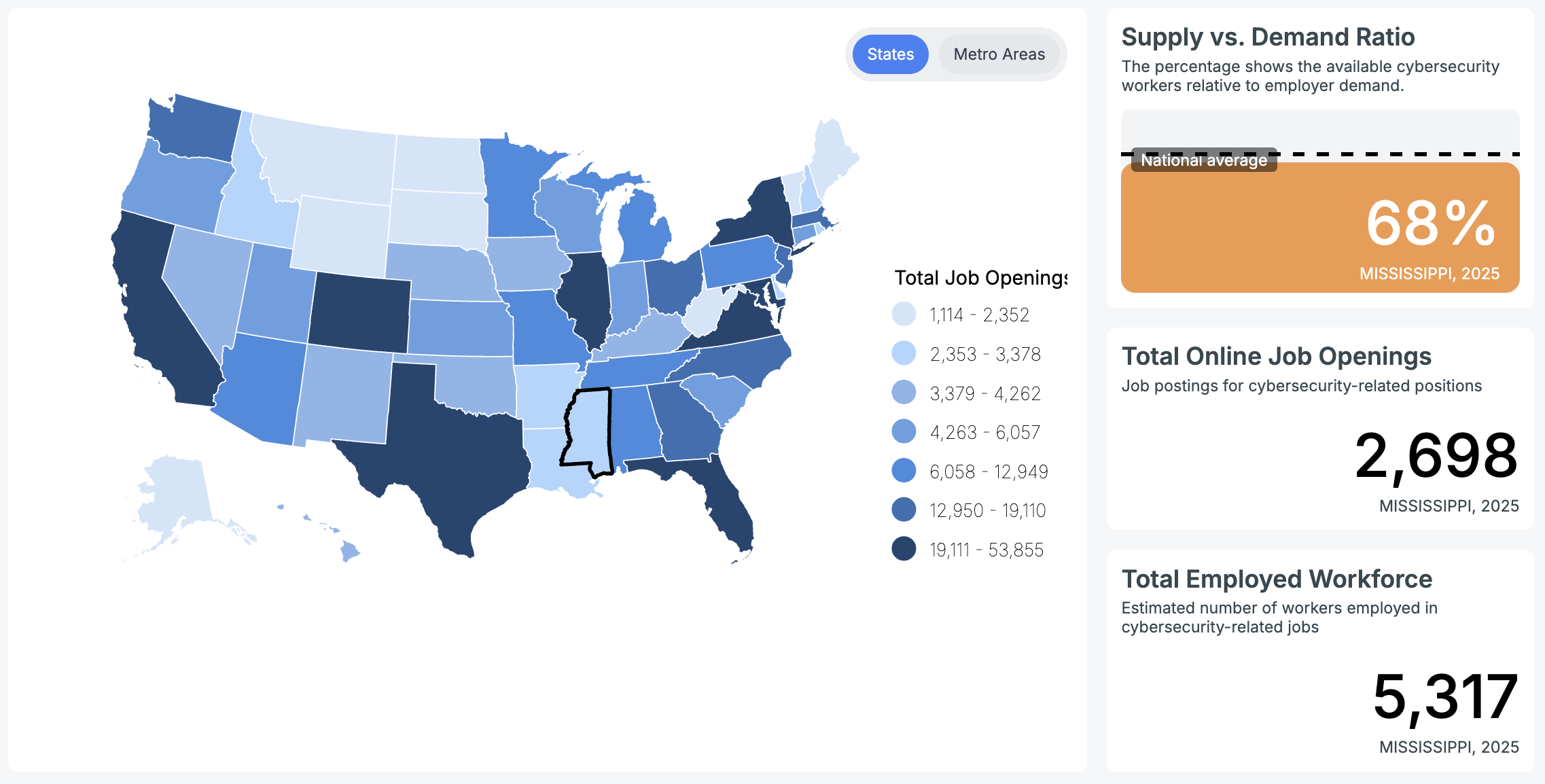
With a total of 2,698 job openings in Mississippi, about 5,317 people sustain employment in the cybersecurity field, according to Cyberseek‘s data.
Some of the top job titles for current employees in the state include:
- Cyber Security Engineer
- Cyber Security Analyst
- Network Engineer / Architect
- Vulnerability Analyst / Penetration Tester
- Incident Analyst / Responder
The Bureau of Labor Statistics shared that the average hourly wage for a cybersecurity analyst in Wyoming was $40.69, with the average annual salary at $84,640.
Cybersecurity in Mississippi
Mississippi’s shift from agricultural production to manufacturing and services makes way for new opportunities in the cybersecurity field.
As state and local governments provide the majority of employment throughout the state, students graduating with computer security and cybersecurity degrees provide the pathway for higher household incomes over the state average.
Although the state stagnates in economic growth, its initiatives in cybersecurity education and policy make way for improvement to the state’s current condition among the nation.