- Bachelor’s degree
- Master’s degree
- Related resources
- Cybersecurity in Delaware
- Growing importance in Delaware
- Jobs in Delaware
This guide is a brief overview of the cybersecurity educational and career opportunities in Delaware.
As the first state, Delaware’s adoption of technology gives its population new opportunities. While the economy’s focused on its abundance of sand and gravel and holding of the country’s biggest chemical manufacturers, jobs in technology, finance, and business make way as the new staple for production.
Initially, Delaware’s ties to the du Pont family helped transform the state into a sizeable chief producer of chemicals, food products, and plastic. Other sectors include agriculture, fishing, and mining as a primary source of GDP income, according to the Department of Labor and Industry.
However, a new economic sector is emerging in Delaware. As mining, chemical production, and business continually slow down due to limited supply, job openings in cybersecurity continue to increase.
Ad
cybersecurityguide.org is an advertising-supported site. Clicking in this box will show you programs related to your search from schools that compensate us. This compensation does not influence our school rankings, resource guides, or other information published on this site.
Featured Cybersecurity Degree Programs
| School Name | Program | More Info |
|---|---|---|
| Southern New Hampshire University | Online BS in Cybersecurity or Online MS in Cybersecurity | website |
| Grand Canyon University | Online BS in Cybersecurity or Online MS in Cybersecurity | website |
| UC Berkeley School of Information | Master’s in Cybersecurity | No GRE/GMAT Required | website |
| University of Maryland Global Campus | Online Bachelor's in Cybersecurity | website |
| Purdue University Global | Online BS in Cybersecurity | website |
Trends in Delaware over the past 12 years have led to increased activities in the finance and business sectors, significantly higher portions than any other state.
More than half of US-based publicly-traded companies reside in Delaware because of its business-friendly corporate law, according to Forbes.
Related resources
Overall, Delaware’s job growth has slowly increased on an annual basis, with Delaware’s leading companies reforming their infrastructure to supply their consumers and match their competitors.
The job market maintains its steady rise through the operation and management of business and government servers, building technology systems, mitigating information technology threats to information systems, and analyzing intelligence.
One impact seen across the state is the adoption of cybersecurity skills in the financial sector. Delaware’s adoption of fintech — financial services delivered through technology — has begun to lower the barriers for new businesses, giving way to many potential opportunities for cybersecurity professionals to grow in their profession and continue to grow the technology sector.
Growing awareness of cybersecurity in Delaware
Delaware is steadily developing cybersecurity resources at the state level.
According to Delaware’s Department of Technology and Information, the state developed the “Delaware Broadband Fund” to support broadband services in public schools and libraries for broadband initiatives.
Delaware’s businesses and government sectors have moved to the cloud for 80 percent of its servers, to create information technology efficiency.
The department also controls cybersecurity for all branches of state government and school networks. The Delaware Information Security Advisory Council began in 2015 to discuss cyber resilience and has since developed cyber partnerships with infrastructure sectors in the state.
Other Delaware state organizations that work on cybersecurity are as follows:
- Delaware Office of Information Technology (OIT): Responsible for the state’s cybersecurity posture. OIT provides security awareness training to state employees, manages the state’s security infrastructure, and responds to cybersecurity incidents.
- Delaware Division of Information Technology Services (ITS): Provides cybersecurity support to state agencies and local governments. ITS offers a variety of services, including risk assessments, security audits, and incident response.
- Delaware Cybersecurity Council (DCC): Public-private partnership that works to improve cybersecurity in Delaware. The council provides resources and support to businesses and organizations and advocates for cybersecurity policies at the state level.
- Delaware Technology Solutions (DTS): Non-profit organization that provides cybersecurity solutions to businesses and organizations in Delaware. DTS offers a variety of services, including managed security services, security awareness training, and vulnerability assessments.
Private sector organizations in Delaware:
- Delaware Technology Council: Trade association that represents the technology industry in Delaware. Provides resources and support to its members, including cybersecurity education and training.
- Delaware Information Security Consortium: A non-profit organization that provides education and training on cybersecurity to Delaware businesses and organizations.
- Delaware Cybersecurity Alliance: A non-profit organization that promotes collaboration and cooperation between the public and private sectors on cybersecurity issues.
Additionally, Delaware formed the Cyberstart Initiative, a program offering information on cybersecurity to high school girls to improve chances to learn about cryptography, digital forensics, and penetration testing as part of a way to increase diversity within the industry.
Cybersecurity education in Delaware
Colleges and universities throughout the state offer both on-campus and online programs that allow students in Delaware and outside of the state to have multiple options for a cybersecurity degree.
Cybersecurity Bachelor’s degrees in Delaware
Bachelor’s degrees in cybersecurity provide the foundation for a professional career in the field, allowing students to gain extensive knowledge in networking infrastructure, computer science, and data management.
Undergraduate students (as well as graduate students) at the University of Delaware can also participate in the Cybersecurity Scholars program, Vertically Integrated Projects, Capture-the-Flag competitions, and more.
- Program: Cybersecurity Minor
CAE designation: CAE-CD
Credits: 126 (18 cybersecurity)
Cost per credit: $424 in-state | $1,139 out-of-state
Delivery Method: Campus
Learn more: Program details
Cybersecurity Master’s degrees in Delaware
A Master’s degree in cybersecurity in Delaware can help you advance your career in this rapidly growing field. Cybersecurity professionals are in high demand, and employers are willing to pay top dollar for qualified candidates.
Campus-based master’s degree
- Program: Master of Science in Cybersecurity
CAE designation: CAE-CD
Credits: 30
Cost per credit: $979
Delivery Method: Campus, Online
GRE/GMAT Required: Required
Learn more: Program details
Online cybersecurity master’s degree
- Program: Online Master of Science in Cybersecurity
CAE designation: CAE-CD
Credits: 30
Cost per credit: $979
Delivery Method: Online
Learn more: Program details - Program: Master of Science in Cybersecurity
CAE designation: CAE-CD
Credits: 36
Cost per credit: $1,536
Delivery Method: Online
Learn more: Program details
The University of Delaware is recognized as a National Center of Academic Excellence for its developments in cybersecurity education, approved by the National Security Agency and the Department of Homeland Security.
Students wishing to apply and complete the program will earn technical skills in cybersecurity that expand on computer engineering, networking protocols, and Python computer programming.
Cybersecurity Jobs in Delaware
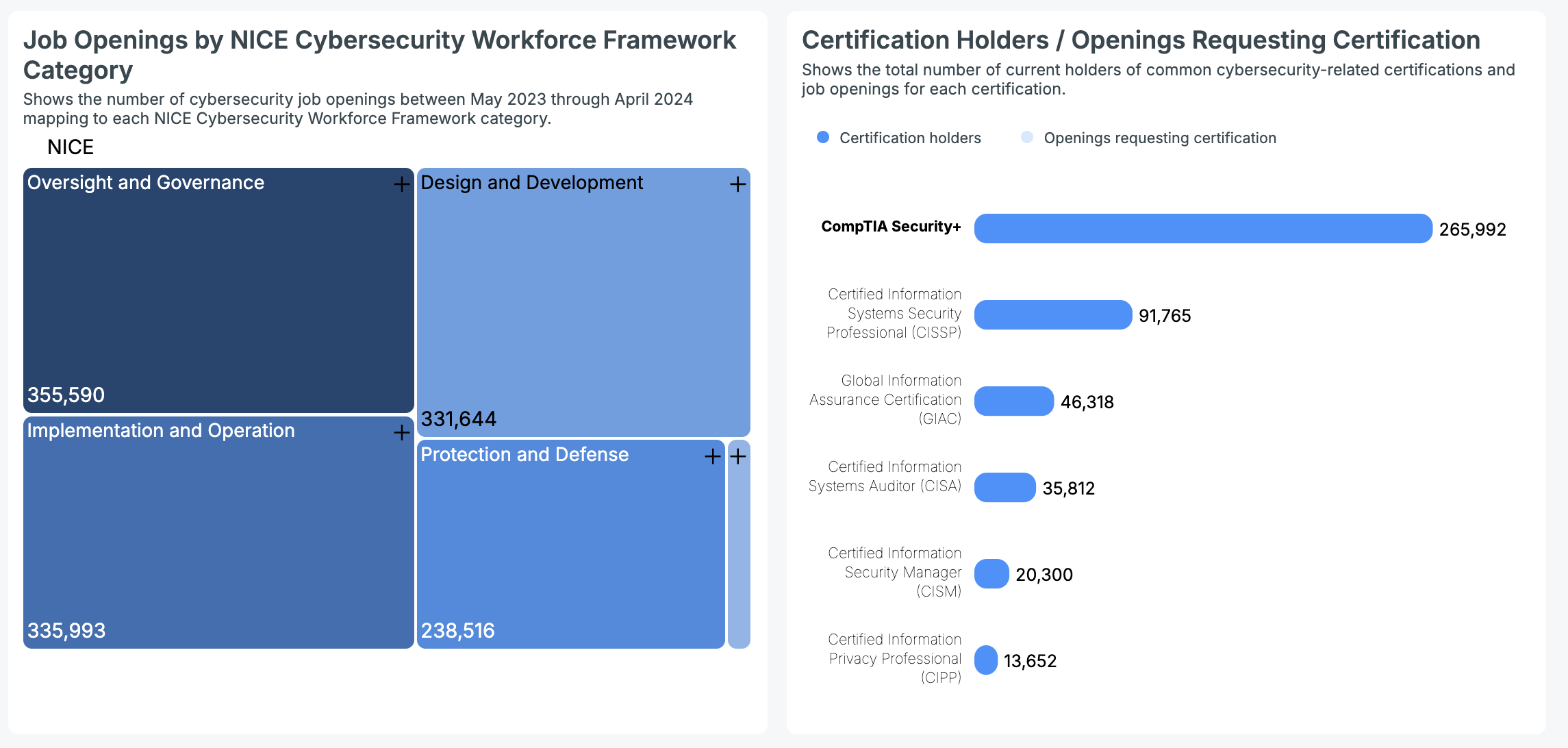
U.S cybersecurity job openings from May 2023 to April 2024, using the NICE Framework, highlighted strong demand for Oversight and Governance (355,590), Implementation and Operation (335,993), and Design and Development (331,644) roles. Protection and Defense positions were also numerous (238,516), contrasting with the much lower demand for Investigation roles (19,525).
Although the state isn’t home to information technology companies, financial companies such as JP Morgan & Chase, Delaware Board of Trade, and Lyapunov Technologies have started hiring cybersecurity professionals.
These companies, through employment, aim to create data management software to find new ways of approaching risk management with sensitive data information.
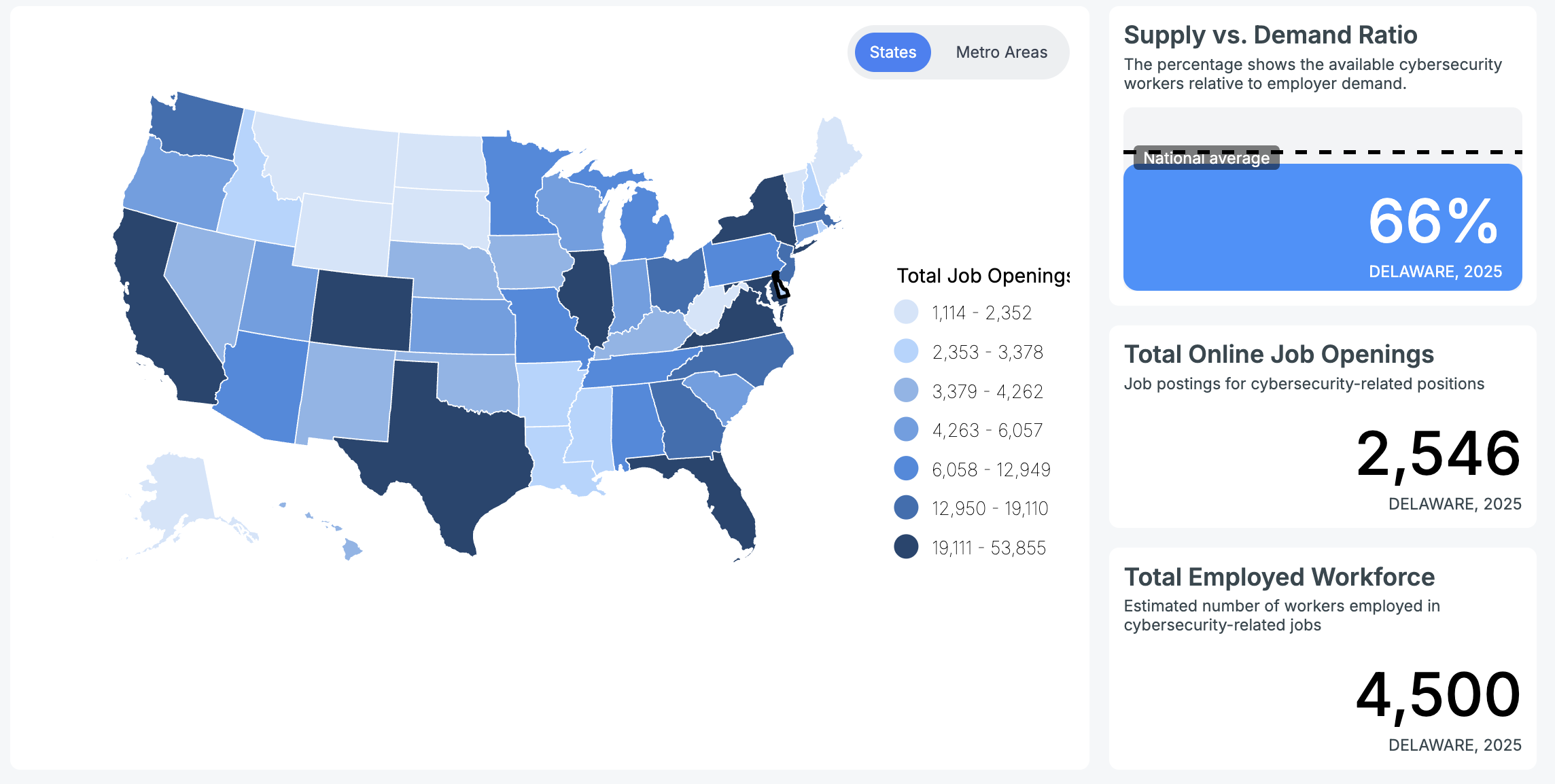
With a total of 2,546 job openings in Delaware, roughly 4,500 people are currently employed in the cybersecurity workforce, according to Cyberseek. The Bureau of Labor Statistics also shared its data that the average hourly wage for a cybersecurity analyst in Delaware is $64.45, while the average annual salary is $134,050.
Here are some of the top job titles in Delaware:
- Cyber Security Engineer
- Cyber Security Analyst
- Vulnerability Analyst/Penetration Tester
- Cyber Security Manager / Administrator
- Cyber Security Consultant
Regarding certifications, the data below shows the current total number of nationwide holders for several common cybersecurity certifications:
- CIPP: 13,652 holders
- CompTIA Security+: 265,992 holders
- CISSP: 91,765 holders
- GIAC: 46,318 holders
- CISA: 35,812 holders
- CISM: 20,300 holders
Cybersecurity in Delaware
Delaware’s transition into information technology moves steadily into the economy; cybersecurity will continue to be in demand regardless of location.
Although the state isn’t known for its cybersecurity systems, government implementation of better data security measures has helped increase the state’s development in its financial sectors.
Internet and digital technologies continue to increase, becoming part of the way corporations and economic handlers communicate, exchange data, and track the supply and demand of their products and services.
Through education programs at Delaware colleges and state initiatives, Delaware can provide unique opportunities for training future employees in the field of cybersecurity threats and other skills in digital technology.