- Associate degree
- Bachelor’s degree
- Master’s degree
- Cybersecurity certifications
- Cybersecurity in Massachusetts
- Jobs in Massachusetts
This guide is a brief overview of the cybersecurity schools in Massachusetts. Included in the guide are other cybersecurity educational opportunities, including online degrees and certification programs.
Massachusetts is best known for Boston, Cape Cod, and Martha’s Vineyard, but this small northeastern state has much more economic muscle than its tight borders would suggest.
Also known as The Bay State, the Commonwealth of Massachusetts has far and away the largest economy in New England. Part of this muscle comes from its centuries-old and rich shipping industry, but the state has reinvented its economy several times over the years.
Ad
cybersecurityguide.org is an advertising-supported site. Clicking in this box will show you programs related to your search from schools that compensate us. This compensation does not influence our school rankings, resource guides, or other information published on this site.
Featured Cybersecurity Degree Programs
| School Name | Program | More Info |
|---|---|---|
| Southern New Hampshire University | Online BS in Cybersecurity or Online MS in Cybersecurity | website |
| Fisher College | Online BS in Information Technology - Cybersecurity | website |
| UC Berkeley School of Information | Master’s in Cybersecurity | No GRE/GMAT Required | website |
| Purdue Global | Online BS in Cybersecurity | website |
| Grand Canyon University | Online BS in Cybersecurity or Online MS in Cybersecurity | website |
Presently, it has thriving business communities in technology, financial institutions, healthcare, education, and tourism. The Boston metropolitan region represents about 80 percent of the state’s economy, including its world-class healthcare and higher education institutions.
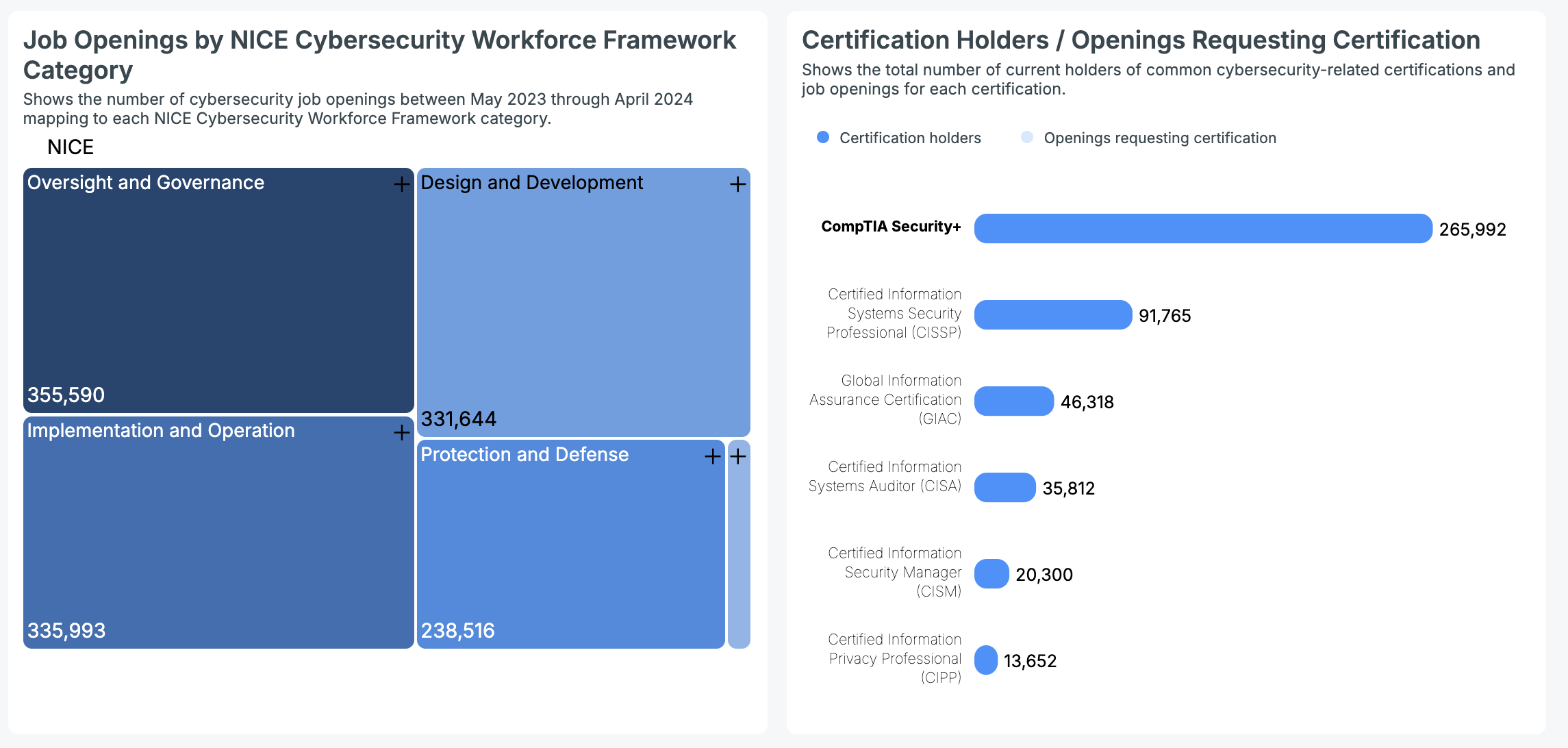
The U.S cybersecurity job market was robust from May 2023 to April 2024. The top three categories by demand were Oversight and Governance (355,590), Implementation and Operation (335,993), and Design and Development (331,644). Protection and Defense roles numbered 238,516, and Investigation roles numbered 19,525.
Related resources
State powers have long adopted the attitude that Massachusetts will take a leadership role in whatever social and economic trends are molding society in general. In the late 20th century it was technology and healthcare. Later the state was at the forefront of environmental legislation, and more recently healthcare insurance for the masses.
One of the key ambitions of the state at present is to become a leading force in cybersecurity, both in terms of its preparation and attracting the best cybersecurity minds and enterprises to reside in Massachusetts.
So while Massachusetts’ rich and storied history is so often the topic of conversation, its present and future appear to be very bright in the cybersecurity department.
The growing importance of cybersecurity in Massachusetts
Healthcare and financial institutions have long been among the leading economic forces in Massachusetts. These days, they are also among the leading targets for cyber hackers.
There are 12 Fortune 500 companies headquartered in Massachusetts. Three of those are financial intermediaries – State Street Corp., Liberty Mutual, and Massachusetts Mutual Life Insurance Company. And the state is a major center for venture capitalists.
Massachusetts made a concerted effort in the late 20th century to attract technology companies of all types and make itself a center of technology. The efforts were successful.
Other members of the Fortune 500 based in Massachusetts include General Electric, Boston Scientific, Raytheon, Biogen, and Thermo Fisher Scientific.
In recent years, the state government has sought to teach government employees and citizens about the dangers of information security breaches. It has also offered educational resources to assist local governments in safeguarding their systems and data.
The state also launched MassCyberCenter in September 2017 to prepare residents and organizations for cyber attacks to foster its cybersecurity ecosystem, and position it as a leader in information security services and research.
Other cybersecurity organizations in Massachusetts:
- Massachusetts Technology Leadership Council (MassTLC): While not solely focused on cybersecurity, MassTLC frequently addresses cybersecurity issues through its various events, seminars, and forums.
- Massachusetts Cybersecurity Strategy Council: Established to advise the governor on future cybersecurity initiatives and how to grow the state’s cybersecurity ecosystem.
- BSides Boston: BSides is a community-driven framework for hosting grassroots cybersecurity conferences worldwide. BSides Boston is the local iteration of this conference.
- Executive Office of Technology Services and Security (EOTSS): A state agency that provides cybersecurity services to state government agencies.
- Attorney General’s Cyber Crimes Division: A division of the Massachusetts Attorney General’s Office that investigates and prosecutes cybercrime.
- Comptroller’s Cybersecurity Center: A division of the Massachusetts Comptroller’s Office that provides cybersecurity services to state government agencies.
Cybersecurity education in Massachusetts
As the state government makes strides to pull Massachusetts into a cybersecurity leadership role, education options are beginning to take root.
One of the big draws for Massachusetts students is the number of quality higher learning institutions, particularly in the Boston area.
Although Massachusetts has made significant progress in cybersecurity education, there is still more work to be done. The digital threat landscape is constantly changing, and the demand for skilled cybersecurity professionals is growing.
Cybersecurity Associate’s degrees in Massachusetts
- Program: Associate in Science in Cybersecurity
Credits: 64-67
Cost per credit: $234 in state | $440 out of state
Delivery Method: Campus
Learn more: Program details
Cybersecurity Bachelor’s degrees in Massachusetts
At a minimum, bachelor’s degrees are now required for most information security career paths. And while a degree in most technology or STEM disciplines is often acceptable, degrees in some cybersecurity disciplines give applicants an upper hand.
Campus-based bachelor’s degree
- Program: Bachelor of Science in Cybersecurity
Credits: 120
Cost per credit: $1,556 in-state | $1,556 out-of-state
Delivery Method: Campus
Learn more: Program details - Program: Bachelor of Science in Cybersecurity
CAE designation: CAE-R, CAE-CO
Credits: 133
Cost per credit: $1,777 in-state | $1,777 out-of-state
Delivery Method: Campus
Learn more: Program details
Online bachelor’s degree
- Program: Online Bachelor's in Cybersecurity
CAE designation: CAE-CD
Credits: 129
Cost per credit: $1,154 in-state | $1,154 out-of-state
Delivery Method: Online
Learn more: Program details
Cybersecurity Master’s degrees in Massachusetts
Master’s degrees in cybersecurity are becoming more common, and are the preferred path for senior cybersecurity professionals in a corporate setting.
For those destined for non-corporate environments, master’s degrees are also highly recommended for careers in cybersecurity consulting, academics, or research. And, of course, continuing to a Ph.D. will help advance an infosec career even further.
Campus-based master’s degree
- Program: Master of Science in Cybersecurity
CAE designation: CAE-R
Credits: 32
Cost per credit: $1,570
Delivery Method: Campus
GRE/GMAT Required: Not required
Learn more: Program details - Program: Master’s in Cyber Security
CAE designation: CAE-R
Credits: 30
Cost per credit: $1,610
Delivery Method: Campus
GRE/GMAT Required: Required
Learn more: Program details
Online master’s degree
- Program: Online MS in Cybersecurity
CAE designation: CAE-CD
Credits: 30
Cost per credit: $880
Delivery Method: Online
GRE/GMAT Required: Not Required
Learn more: Program details - Program: Master of Science in Cybersecurity
CAE designation: CAE-R
Credits: 32
Cost per credit: $1,570
Delivery Method: Online
GRE/GMAT Required: Not Required
Learn more: Program details
Cybersecurity PhD degrees in Massachusetts
- Program: Ph.D. in Cybersecurity
CAE designation: CAE-R
Credits: 48
Cost per credit: $1,625
Delivery Method: Campus
GRE/GMAT Required: Optional
Learn more: Program details
Cybersecurity certifications in Massachusetts
Some cybersecurity certifications are designed to provide an introduction to information security and potentially a foot in the door, or at least a step up on attaining a degree.
Other certification programs are intended for those currently working in cybersecurity to further their education, or even as a substitute to a full advanced degree.
Both types of certificates are available through Massachusetts learning institutions, with an emphasis on advanced certificates.
- Program: Cybersecurity Certificate
Credits: 22
Cost per credit: $220 in state | $426 out of state
Delivery Method: Online
Learn more: Program details - Program: Cybersecurity Certificate
Credits: 27
Cost per credit: $24 in state | $230 out of state
Delivery Method: Campus
Learn more: Program details - Program: Advanced Cybersecurity Certificate
Credits: 24
Cost per credit: $234 in state | $440 out of state
Delivery Method: Hybrid
Learn more: Program details - Program: Cyber Security Certificate
Credits: 24
Cost per credit: $25 in state | $230 out of state
Delivery Method: Campus
Learn more: Program details - Program: Cyber Security Certificate
Credits: 27
Cost per credit: $211 in state | $417 out of state
Delivery Method: Campus
Learn more: Program details - Program: Certificate of Completion in Cybersecurity
Credits: 28
Cost per credit: $25 in state | $242 out of state
Delivery Method: Online
Learn more: Program details
Drawing from Cyberseek’s comprehensive national data, we can see that the current count of professionals with leading cybersecurity certifications is as follows:
- CompTIA Security+: 265,992 holders
- CISSP: 91,765 holders
- GIAC: 46,318 holders
- CISA: 35,812 holders
- CISM: 20,300 holders
- CIPP: 13,652 holders
Cybersecurity bootcamps in Massachusetts
- Program: Cybersecurity Bootcamp
CAE designation: CAE-CD
Credits: 6 months
Cost per credit: $4,275
Delivery Method: Online
Learn more: Program details - Program: Cybersecurity Boot Camp
CAE designation: CAE-R
Credits: 24 Weeks
Cost per credit: $4,275
Delivery Method: Online
Learn more: Program details
Cybersecurity jobs in Massachusetts
Among Northeast US states, Massachusetts and New York stand out as hot spots for cybersecurity activity. What Massachusetts lacks in physical size, it makes up for in economic power. And the focus of the economy is one reason cybersecurity is so critical.
Healthcare and education organizations were by far the largest employers in the state in 2019, while the second largest employment sector in Massachusetts is professional and business services, also prolific sources of confidential data.
Healthcare companies have become a favored target for hackers due to the large amount of personal and confidential information they procure and store.
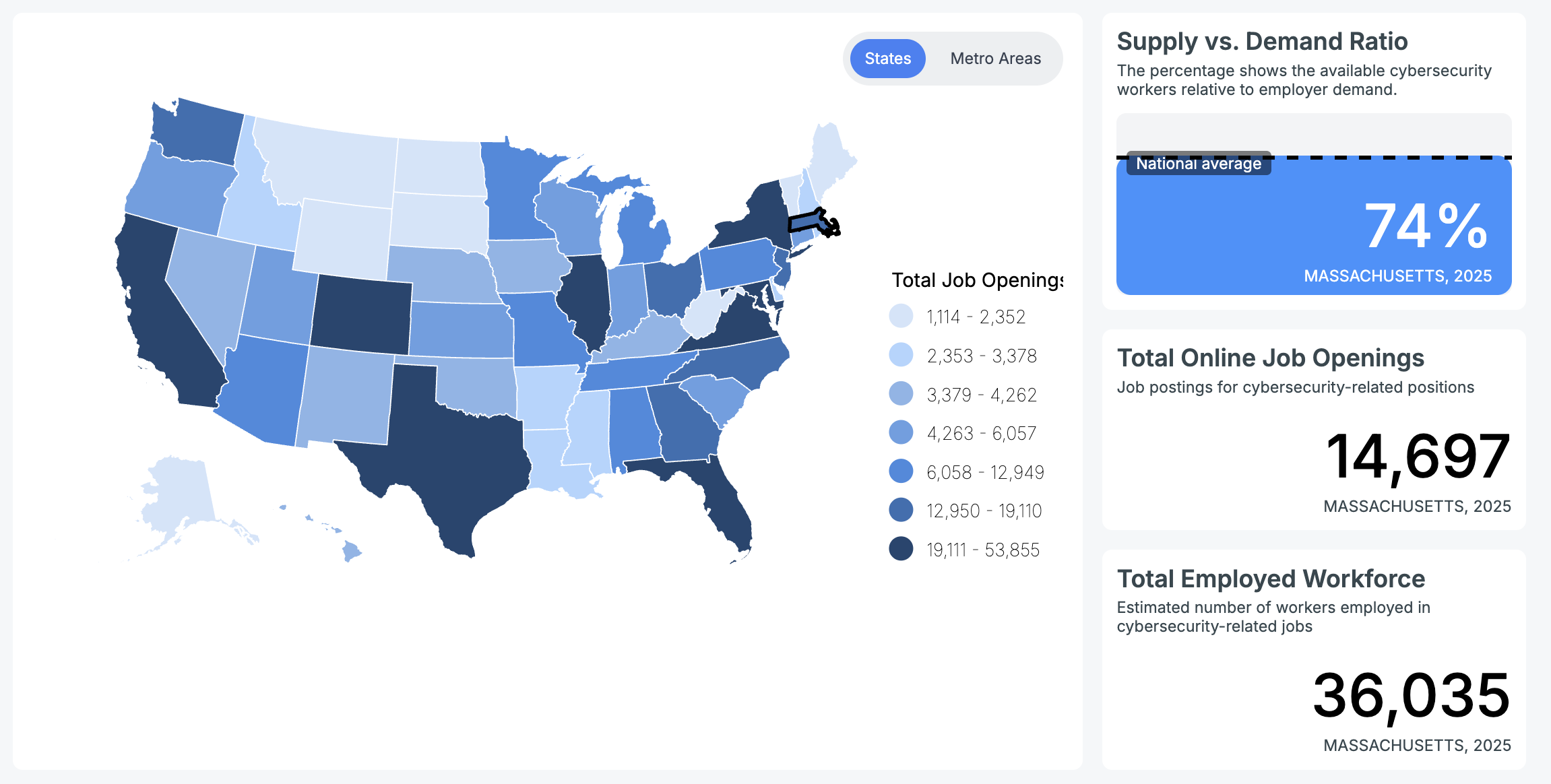
According to Cyberseek, Massachusetts had just over 36,035 people employed in cybersecurity-related positions and about 14,697 cybersecurity job openings were posted.
Of those openings, more than 13,431 were in the Boston metropolitan area. Boston has an extremely high concentration of health and education institutions, not to mention being the second biggest financial center in the Northeast behind New York City.
The Bureau of Labor Statistics reports that cybersecurity analysts in Massachusetts earned an average of $61.35 per hour and an average annual salary of $127,610.
Both pay rates are well above the national averages. The one downside of Massachusetts is its high standard of living and high tax burden. Both are among the highest in the country.
Still, there will be plenty of lucrative employment opportunities in Massachusetts, and the Boston area in particular, for years to come.
The list of cybersecurity job titles in Massachusetts is headlined by the following:
- Cybersecurity Engineer
- Cybersecurity Analyst
- Cybersecurity Administrator/Manager
- Software Developer/Engineer
- Cybersecurity Consultant
- Penetration Tester/Vulnerability Assessor
- Network Engineer/Architect
- Systems Engineer
- IT Auditor
Cybersecurity in Massachusetts
Since its earliest days, even as a colony, Massachusetts has always defied its small size and been a major force economically. While its access to the Atlantic Ocean has provided an advantage, the people of Massachusetts continue to adopt an attitude of leadership.
Today, the Commonwealth is determined to be a leader in cybersecurity, and there is no reason to doubt that it will accomplish just that.
The state certainly has plenty of highly regarded and even elite colleges and universities to train and educate tomorrow’s cybersecurity leaders. And the government is fully behind in developing the technology and capacity to keep Massachusetts’ information safe.
Like everywhere else, there is already a shortage of qualified professionals, and demand is growing rapidly.