- Career steps
- Career overview
- Important skills
- What do security specialist do?
- Job description
- Salary and outlook
There are many pathways that people take to become a cybersecurity specialist, but they all involve some combination of education, specialized training, and experience.
Ad
cybersecurityguide.org is an advertising-supported site. Clicking in this box will show you programs related to your search from schools that compensate us. This compensation does not influence our school rankings, resource guides, or other information published on this site.
Featured Cybersecurity Training
| School Name | Program | More Info |
|---|---|---|
| Purdue Global | Online BS in Cybersecurity | website |
| UC Berkeley School of Information | Online Master’s in Cybersecurity | No GRE/GMAT Required | website |
| Southern New Hampshire University | Online BS in Cybersecurity or Online MS in Cybersecurity | website |
One of the primary responsibilities of a cybersecurity specialist is to keep tabs on the systems employed by their organization and report any issues to management. They are also responsible for anticipating future threats and advising on how to deal with them.
What is a cybersecurity specialist?
A cybersecurity specialist might wear many hats depending on the size and shape of his or her company or organization. As the job title implies, cybersecurity specialists are expected to have a certain level of training and expertise that allows them to give advice and training on the latest digital best practices.
Sometimes, cybersecurity specialists might have detailed expertise on a particular vendor’s product (such as CISCO Systems, which makes networking and IT products), or they might have experience in other domains such as computer operating systems or mobile applications.
Common job titles related to this role:
- Cybersecurity Specialists
- Information Security Specialists
- Security Specialists
- Cybersecurity Analysts
- Privacy Specialists
A simple way of thinking about a cybersecurity specialist is someone who keeps tabs on a company’s or organization’s security while also helping other employees and teammates stay current on best practices.
This role is critical because oftentimes data breaches come from inside the organization, either intentionally or accidentally.
Four key steps to becoming a cybersecurity specialist
1. Education: Like most other careers in cybersecurity, most jobs falling under the cybersecurity specialist category require some form of formal education. However, since cybersecurity specialist jobs can fall across a wide spectrum of job descriptions and responsibilities, it is possible to obtain a specialist job after completing many levels of cybersecurity education.
Cyberseek reports that 11 percent of cybersecurity specialists have an associate’s degree, 44 percent bachelor’s degree, and 45 percent have a graduate degree. In other words, there are cybersecurity specialist jobs for people completing a cybersecurity associate’s degree, a bachelor’s degree, or a master’s degree.
Additionally, much of the cybersecurity specialist workforce found employment after completing a related degree (such as computer science, engineering, or mathematics) and/or by having closely related work experience.
2. Industry certifications and clearances: Again, as is the norm in many other cybersecurity career paths, obtaining the proper industry certifications and/or clearances is an important step in career preparation.
It makes sense to start thinking about what kinds of certifications are required by an employer, or what kinds of certifications make job applicants competitive within the field.
To get an idea of some of the kinds of cybersecurity certifications available, here are a few examples:
Security+ is a CompTIA certification that is considered a basic cert among cybersecurity professionals. It covers the topics of risk management and threat assessment.
Network + is also offered by CompTIA this certification (like the name implies) focuses on networking infrastructure and operations. It is considered a foundational certification.
SANS/GIAC Certification focuses on cloud security, cyber defense, offensive operations digital forensics & incident response, industrial control systems, and security management.
The Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP) is a more advanced certification designed for cybersecurity professionals with at least five years of work experience. The certification covers topics such as architecture, engineering, and management.
Certified Information Security Manager (CISM) is offered by ISACA and is geared towards management more than the technical side, but it can be useful for those aiming for a leadership role in security software development.
Certified Information Systems Auditor (CISA): Also from ISACA, is more audit-focused but is valuable for those wanting to understand security from an assurance perspective.
These are just a few examples of the dozens of cybersecurity certifications available. When looking at job opportunities in the cybersecurity industry, it’s a good idea to keep notes about what kinds of certifications employers are looking for.
Additionally, when interviewing for cybersecurity specialist positions, it’s a good idea to ask potential employers about what kinds of professional development opportunities are available including what kinds of certifications an employer will pay for.
3. Experience: Another important aspect of obtaining a job as a cybersecurity specialist is demonstrating relevant experience.
This can take the form of other, related work experience, or it can take the form of a structured internship or other formal hands-on learning.
4. Network: Looking for opportunities to grow a professional network is always a good idea.
There are several network-oriented professional cybersecurity organizations and groups that are specifically designed to alert members about job openings and professional development opportunities.
What do cybersecurity specialists do?
Cybersecurity specialists create and implement security audits across computer hardware and software systems. They make sure that the systems perform the way they are supposed to, and that they are safe from attack.
Often the job of a cybersecurity specialist can be somewhat routine. They are responsible for making sure that networks and computer systems are up-to-date and not vulnerable to software bugs.
In addition, security specialists are also responsible for making sure that other co-workers are kept up-to-date on security best practices, which means they might take on the role of a trainer or an advisor.
Another aspect of a cybersecurity specialist’s job is the design of firewalls and other security measures to make sure that information and proprietary networks are compliant with the most recent security standards.
Cybersecurity specialists are also responsible for continually monitoring security systems and networks for anomalies and tracking those activities in documents and reports.
Cybersecurity specialist skills and experience
Cybersecurity specialists play an interesting role in the companies and organizations where they are employed. People in this role are often hired as much for their soft skills as their technical ability.
Cybersecurity specialists need to be able to communicate well and be comfortable in team roles. The job often entails coaching and training co-workers on security best practices.
Additionally, cybersecurity specialists are often called on in times of crisis or emergency — or when there are issues with networks or data systems. So the ability to thrive under “emergency” situations is important.
Finally, holding the position of security specialist might require helping co-workers adopt new technologies and security software as it develops. However, most people are reluctant to change, especially if it requires learning a new operating procedure or workflow. So the ability to articulate the reason for the change and the ability to relate to co-workers’ needs and objections is also important.
Cybersecurity specialists need to be comfortable in a world that is constantly moving and shifting. New digital attack vectors and mechanisms are popping up all of the time, and a cybersecurity specialist is tasked with figuring out what kinds of skills and experience are required to protect against those emerging threats.
That often means that continuing education is required — both in the form of formal, industry-recognized certifications — and in the form of informal learning and tracking industry developments.
In terms of skills, experience, and general mindset, a cybersecurity specialist needs to be like a Swiss Army knife of the digital world. A person in this role needs to be multi-disciplinary and adaptable to a wide variety of situations.
According to Cyberseek, here is the list of the top skills and future skills for cybersecurity specialists:
Projected future skills for cybersecurity specialist:
- Threat Hunting
- Risk Management Framework
- Threat Intelligence & Response
- Network Firewalls
- Phishing
Top skills for cybersecurity specialist:
- Cyber Security
- Vulnerability
- Auditing
- Computer Science
- Information Systems
- Incident Response
- Security Controls
- Firewall
- IT Security
Outlook for cybersecurity specialists
The employment of information security analysts, which includes cybersecurity specialists, is predicted to grow 33 percent by 2033, much faster than the average for all occupations.
Several factors are driving this growth. First, the increasing reliance on technology in all aspects of our lives has created more opportunities for cybercriminals to attack.
Second, the growing sophistication of cyberattacks means that organizations need more skilled cybersecurity professionals to protect themselves. Third, the global shortage of cybersecurity workers is expected to continue, which will drive up wages and salaries for cybersecurity specialists.
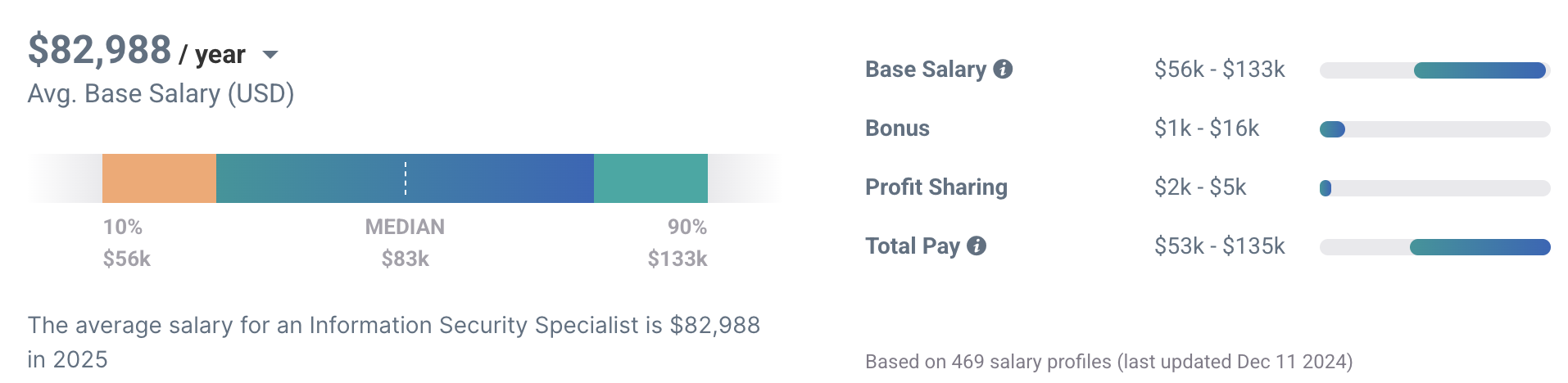
How much do security specialists make?
According to a recent PayScale questionnaire, most employees with the job title cybersecurity specialists responded that they have a high level of job satisfaction.
Payscale also reports that in 2025, cybersecurity specialists will be compensated across a wide range, depending on experience, responsibilities, and geography. The pay for a specialist ranges from $56,000 to $133,000. The average pay is $82,988.
Looking for more information about careers in cybersecurity? Learn more.
Frequently asked questions
A cybersecurity specialist is a professional who is responsible for protecting computer systems, networks, and data from unauthorized access, theft, or damage. They work to prevent cyber attacks, detect security breaches, and respond to security incidents.
Specific responsibilities of a cybersecurity specialist may vary depending on their job title, organization, and industry. However, some common responsibilities may include: assessing and managing risk, designing and implementing security measures, monitoring and detecting security breaches, investigating security incidents, developing security policies and procedures, and providing training and awareness programs for employees.
Like most other careers in cybersecurity, it’ll be a great start to earn your degree relating to the cybersecurity specialist category and then get industry certifications, clearances, and practical experience.
The outlook for cybersecurity specialists is very positive due to the increasing reliance on technology and the growing threat of cyber attacks. As organizations continue to invest in cybersecurity to protect their data and systems, the demand for skilled cybersecurity professionals is expected to continue to increase in the years to come.
To be a successful cybersecurity specialist, one should have knowledge and skills in areas such as network security, cryptography, risk management, compliance, incident response, and threat analysis. They must stay up to date with the latest trends and threats in the cybersecurity industry and be able to adapt to evolving security risks. Good communication, problem-solving, and analytical skills are also important for a cybersecurity specialist.
Sources
- Outlook info for Security Analyst | Sourced from Bureau of Labor Statistics in Feb 2025
- Cybersecurity Specialist career pathway | Sourced from cyberseek.org in Feb 2025
- Salary information for Cybersecurity Specialist | Sourced from Payscale.com in Feb 2025