While many states have a robust manufacturing economy, Tennessee is especially proud if its advanced manufacturing industry.
With the likes of Nissan, LG, and Porter-Cable calling the state home, Tennessee is one of America’s most important producers of high-tech durable goods.
Ad
cybersecurityguide.org is an advertising-supported site. Clicking in this box will show you programs related to your search from schools that compensate us. This compensation does not influence our school rankings, resource guides, or other information published on this site.
Featured Cybersecurity Degree Programs
| School Name | Program | More Info |
|---|---|---|
| Purdue Global | Online BS in Cybersecurity | website |
| Southern New Hampshire University | Online BS in Cybersecurity or Online MS in Cybersecurity | website |
| East Tennessee State University | Online Master's of Business Administration - MBA in Cybersecurity Management | website |
| UC Berkeley School of Information | Master’s in Cybersecurity | No GRE/GMAT Required | website |
| Grand Canyon University | Online BS in Cybersecurity or Online MS in Cybersecurity | website |
A glance at the numbers further illustrates Tennessee’s commitment to production. Advanced manufacturing accounts for more than 170,000 jobs in the state, and more than $10 billion has been invested in manufacturing in just the last five years.
That’s a lot of capital to invest, but the returns have been far from paltry. Each year, Tennessee exports over $24 billion worth of manufactured goods.
All of that manufacturing infrastructure has certain requirements, though. Mostly lots of electricity. Tennessee is the 20th highest consumer of electricity per capita in the United States and that electricity must come from somewhere.
The Tennessee Valley Authority is “the nation’s largest government-owned power provider.” Through a combination of nuclear, coal, solar, wind, and natural gas the TVA annually sells approximately 150 billion kilowatt-hours of electricity.
That energy production facilitates manufacturing, but it also makes Tennessee a tempting target for cyber terrorists. A disruption to the increasingly digitized power grid could lead to costly outages as manufacturers are forced to shut down.
Thankfully, the TVA is well aware of the threat posed. They employ more than 50 cybersecurity specialists who actively scan for threats to keep the grid safe.
It’s not cheap to employ a small company’s worth of cybersecurity technicians; however, the TVA recognizes the technicians’ importance. All things considered, Tennessee has proven to be a state that’s aware of just how important cybersecurity is in the digitized 21st century.
Cybersecurity in Tennessee
FutureCon is Tennessee’s premier cybersecurity conference. It’s an annual event that
“brings high-level Cyber Security Training, discovering cutting-edge security approaches, managing risk in the ever-changing threat of the cybersecurity workforce.”
Attendees can learn advanced techniques to combat cybercrime as well as gain a new perspective on what some of America’s top CTOs are doing to keep their digital empires safe.
This information may prove especially useful as cybercriminals are constantly developing new techniques to subvert existing security systems. Thus, cybersecurity technicians have a responsibility to stay up-to-date with the latest industry best practices.
In addition to the conference, the city of Nashville keeps an up-to-date website rich with cybersecurity resources. The website offers a perspective on everything from phishing scams to careers in cybersecurity to data privacy best practices.
As one would expect from a state with a strong focus on digital security, Tennessee has several educational opportunities for those who would like to pursue a career in cybersecurity.
Cybersecurity educational opportunities in Tennessee
When pursuing an associate’s degree, a student can expect to be exposed to a wide range of subject material. Besides the content related to their cybersecurity major, they may also study psychology, English, or math.
Candidates with only an associate’s degree may find it difficult to begin a career in cybersecurity. However, there are positions available for those with an associate’s degree, especially in fields like computer science or information technology.
Related resources
Cybersecurity associate degrees in Tennessee
There are three associate’s degrees in Tennessee. These degrees are offered by a community college. Currently, only one associate’s degree in cybersecurity is offered online in Tennessee.
- Program: Associate of Applied Science in Computer Information Systems: Cyber Defense Concentration
CAE designation: CAE-CD
Credits: 60
Cost per credit: $176 in state | $726 out of state
Delivery method: Campus
Learn more: Program details - Program: A.A.S. in Computer Information Technology – Cyber Defense Concentration
Credits: 60
Cost per credit: $226 in state | $776 out of state
Delivery method: Campus & online
Learn more: Program details - Program: Associate of Applied Science Computer Information Tech: Cyber Defense
CAE designation: $176 in-state | $726 out of state
Credits: 63
Cost per credit: $176 in-state | $726 out of state
Delivery method: Campus
Learn more: Program details
Cybersecurity bachelor’s degrees in Tennessee
Any job seeker who would like to seriously pursue a career in cybersecurity should consider a bachelor’s degree as the minimum level of education necessary to secure good work.
A four-year bachelor’s degree exposes students to considerably more than a two-year associate’s. Students will learn how to deal with a wide range of cybersecurity threats and they may minor in a specific area of cybersecurity, such as network infrastructure or cyber forensics.
Four universities offer campus-based bachelor’s degree programs in Tennessee. Unfortunately, there is just one online cybersecurity bachelor’s degree in Tennessee. For more information please see the list below.
- Program: Major Criminal Justice ( Cyber Defense/Cyber Security Concentration)
CAE designation: CAE-CD
Credits: 120
Cost per credit: $427 in-state | $427 out-of-state
Delivery method: Campus
Learn more: Program details - Program: Bachelor of Science in Computer Science – Cyber Security
CAE designation: CAE-CD
Credits: 120
Cost per credit: $451 in state | $626 out of state
Delivery method: Campus
Learn more: Program details - Program: Bachelor of Science in Computer Science: Cyber Security
CAE designation: CAE-CD
Credits: 120
Cost per credit: $550 in-state | $672 out-of-state
Delivery method: Campus
Learn more: Program details - Program: B.S. Computer Science Cybersecurity Concentration
CAE designation: CAE-CD, CAE-R
Credits: 120
Cost per credit: $355 in state | $540 out of state
Delivery method: Campus & online
Learn more: Program details
Cybersecurity master’s degrees in Tennessee
A master’s degree builds on a bachelor’s, further exposing students to cybersecurity detection, prevention, and investigation techniques. For instance, master’s degree students typically learn cyber forensics and evidence collection to catch cybercriminals.
Most master’s degree programs require a cybersecurity or computer science undergraduate degree. Master’s students may choose to pursue specialized areas of knowledge like cryptography or ethical hacking.
Students interested in taking a master’s degree in cybersecurity in Tennessee can enroll in one university that offers the degree. Please see the list below for more information.
- Program: MS in Computer Science - Applied Cybersecurity
Credits: 72
Cost per credit: $704 in-state | $799 out of state
Delivery method: Online
GRE requirement: Not required
Learn more: Program details
Cybersecurity PhD degrees in Tennessee
A PhD degree is the highest level of education possible in the cybersecurity field. A PhD will all but guarantee the graduate a great job with plenty of opportunities for advancement.
There is only one cybersecurity-specific PhD option in Tennessee.
- Program: Ph.D. in Computer Science – Cybersecurity
Credits: 72
Cost per credit: $751 in state | $1011 out of state
Delivery method: Campus
GRE requirement: Not required
Learn more: Program details
Cybersecurity certifications in Tennessee
Cybersecurity certifications may be required for certain jobs and can help any candidate increase their chance of getting hired.
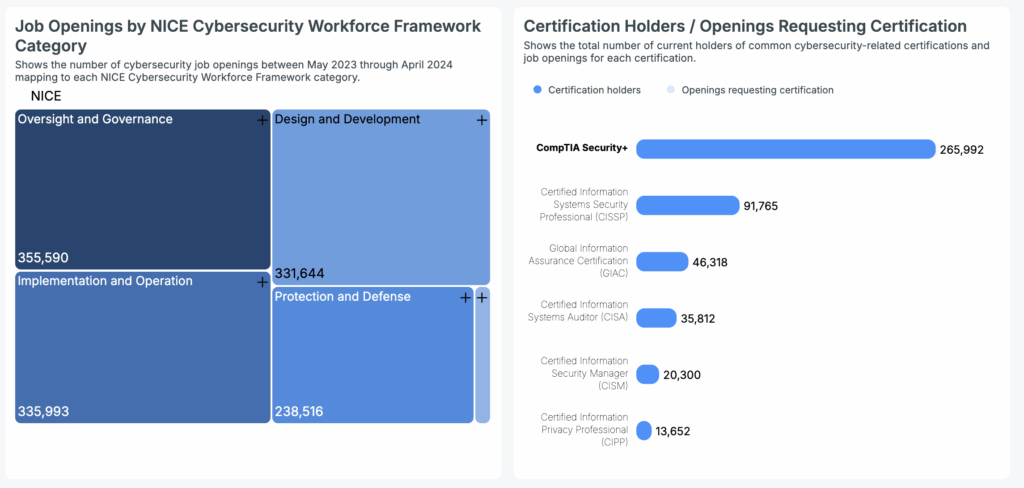
For a clear understanding of cybersecurity certification prevalence nationwide, Cyberseek’s data indicates:
- CompTIA Security+: 265,992 certification holders
- CISSP: 91,765 certification holders
- GIAC: 46,318 certification holders
- CISA: 35,812 certification holders
- CISM: 20,300 certification holders
- CIPP: 13,652 certification holders
Currently, Tennessee has one certification program available to students. More information is available in the list below.
- Program: Graduate Certificate in Cybersecurity and Information Assurance
CAE designation: CAE-CD, CAE-R
Credits: 12
Cost per credit: $532 in-state | $755 out of state
Delivery method: Online
Learn more: Program details
Cybersecurity jobs in Tennessee
The cybersecurity sector maintained a high level of demand across the United States from May 2023 to April 2024.
Job openings were most concentrated in Oversight and Governance (355,590). Other prominent areas included Implementation and Operation (335,993) and Design and Development (331,644). Protection and Defense roles accounted for 238,516 openings, while Investigation roles comprised 19,525.
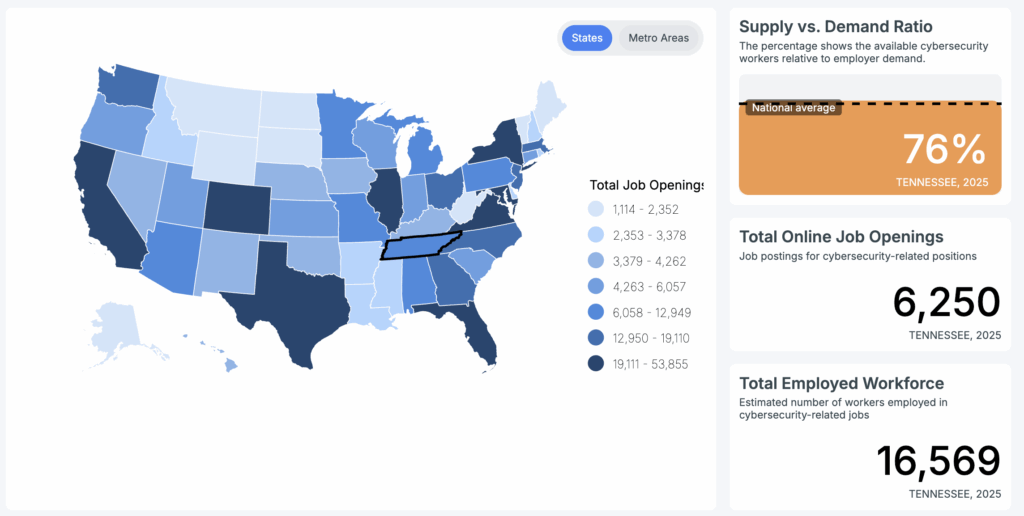
According to CyberSeek‘s data, a cybersecurity job placement data aggregator, there are 6,250 cybersecurity positions open in the state of Tennessee, with 16,569 currently employed.
Due to the continued growth of cybercrime and the increasing digitization of everything from refrigerators to self-driving cars, the demand for cybersecurity technicians is rising. A person who begins studying at university today is very likely to find a job once they graduate in four years.
The annual mean wage for cybersecurity technicians in Tennessee is $100,990 ($48.55/hr), as shared by the BLS. That salary makes a cybersecurity career look especially lucrative, even compared to other IT positions.
Cybersecurity in Tennessee
Billions of dollars have been invested to modernize Tennessee’s manufacturing industry. The result is an advanced manufacturing economy that relies heavily on robotic, digitally-controlled assembly.
While such systems are extremely efficient, they’re also susceptible to hacking and other forms of cyber tampering.
This has not been lost on Tennessee’s leading companies, and the demand for cybersecurity specialists is strong.
Whether it’s safeguarding proprietary manufacturing data or protecting an extensive electrical grid from cyber interference, a person with a cybersecurity degree in Tennessee can expect to find a job that matches their expertise.
Frequently Asked Questions
Tennessee’s advanced manufacturing industry—including companies like Nissan and LG—relies on robotics and digital systems, making it a prime target for cyberattacks.
The TVA employs more than 50 cybersecurity specialists to safeguard the power grid, ensuring stable energy for manufacturing and households across Tennessee.
Associate programs are offered at Jackson State Community College, Motlow State Community College, and Roane State Community College, with one online option.
Students can pursue bachelor’s programs at LeMoyne-Owen College, Tennessee Tech University, University of Tennessee at Chattanooga, and the University of Memphis.
Yes. Only one online cybersecurity bachelor’s degree is currently available in the state, providing flexible learning for working professionals.
The University of Tennessee in Knoxville offers a cybersecurity master’s program focused on prevention, detection, and digital forensics.
Yes. The University of Tennessee provides the state’s only cybersecurity-specific PhD program, designed for research and academic leadership.
Top certifications include CompTIA Security+, CISSP, GIAC, CISA, CISM, and CIPP, all highly recognized by employers in Tennessee.
Nashville State Community College and the University of Memphis provide certification training to help professionals upskill and meet employer demands.
FutureCon is the state’s premier cybersecurity conference, offering hands-on training, networking, and insights from industry leaders.
According to CyberSeek, Tennessee has about 6,250 open cybersecurity positions, with more than 16,500 employed in the workforce.
Cybersecurity technicians earn an average annual salary of $100,990 ($48.55/hr), higher than many other IT positions in the state.
Energy, advanced manufacturing, financial services, and healthcare are top industries requiring robust cybersecurity protection.
Yes. Nashville offers cybersecurity awareness programs, online resources, and is home to major employers hiring infosec professionals.
With strong industry demand, excellent universities, competitive salaries, and low cost of living, Tennessee offers a rewarding environment for cybersecurity careers.