- Associate degrees
- Bachelor’s degrees
- Master’s degrees
- Cybersecurity certifications
- Cybersecurity initiatives
- FAQs
Students researching a cybersecurity degree in Ohio, comparing a cybersecurity school in Ohio, or evaluating cybersecurity programs in Ohio will find a broad range of associate, bachelor’s, and graduate pathways aligned with employer demand across the state. This page focuses specifically on degree and school options in Ohio and references institutions only when they offer distinctive workforce, research, or training initiatives that go beyond a standard program listing.
How we keep this page current
This page is updated using data from CyberSeek, the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), the Ohio Department of Job and Family Services—Labor Market Information (LMI) office, the State of Ohio Office of Information Technology, and the National Science Foundation (NSF) Scholarship for Service (SFS) program.
All institutional references are verified against official university or state pages. Statistical claims are cited inline, and time-sensitive metrics are reviewed periodically and revised or removed as needed.
Ad
cybersecurityguide.org is an advertising-supported site. Clicking in this box will show you programs related to your search from schools that compensate us. This compensation does not influence our school rankings, resource guides, or other information published on this site.
Featured Cybersecurity Degree Programs
| School Name | Program | More Info |
|---|---|---|
| Purdue Global | Online BS in Cybersecurity | website |
| Southern New Hampshire University | Online BS in Cybersecurity or Online MS in Cybersecurity | website |
| Herzing University | Online BS in Cybersecurity | website |
| UC Berkeley School of Information | Master’s in Cybersecurity | No GRE/GMAT Required | website |
| University of Maryland Global Campus | Online Bachelor's in Cybersecurity | website |
| Grand Canyon University | Online BS in Cybersecurity or Online MS in Cybersecurity | website |
Cybersecurity workforce demand in Ohio
Workforce data provides important context for students evaluating cybersecurity programs in Ohio.
According to CyberSeek’s state-level dashboard, Ohio consistently ranks among the states with high cybersecurity employer demand, with thousands of active job postings for cybersecurity-related roles in recent reporting periods. CyberSeek’s data reflects employer job postings and workforce supply-demand ratios.
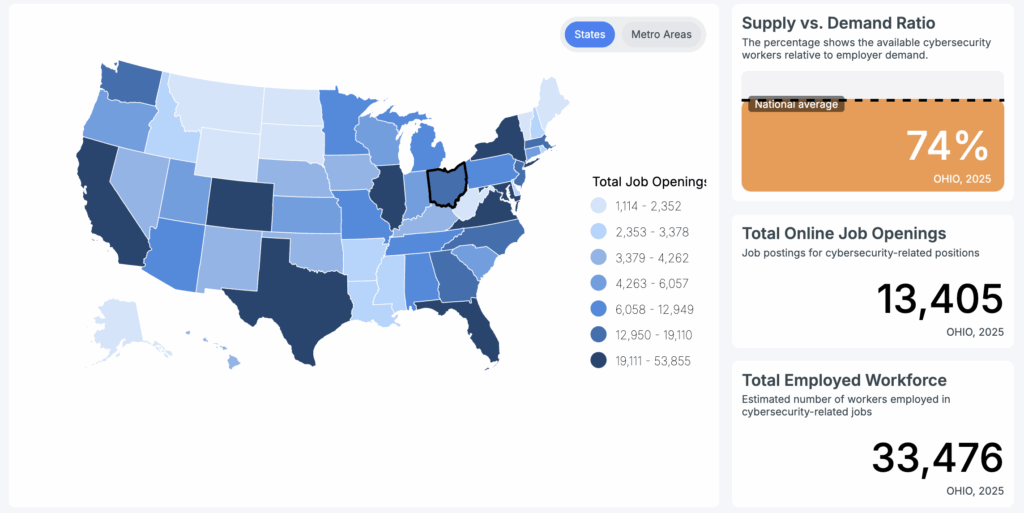
The Ohio Department of Job and Family Services (ODJFS) Labor Market Information office provides long-term projections for computer and mathematical occupations, including roles aligned with information security analysis and cybersecurity. These projections indicate continued expected growth across the decade.
The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) reports that, as of May 2024, Ohio employs thousands of information security analysts, with a mean annual wage well above the state’s overall average wage level. For comparison, BLS also reports strong employment levels in related occupations such as computer systems analysts in Ohio.
It is important to understand that:
- CyberSeek job postings measure hiring activity and employer demand signals.
- BLS employment estimates measure filled positions.
These data sources reflect different aspects of the labor market and should not be interpreted as identical metrics.
Related resources
Cybersecurity degree pathways in Ohio
Ohio offers multiple academic entry points into cybersecurity, from two-year technical programs to research-focused graduate degrees. The right pathway depends on prior education, technical background, and career goals.
Associate degrees
Associate degrees in cybersecurity, information assurance, or network security typically require two years of full-time study. Programs often emphasize:
- Network configuration and defense
- Secure systems administration
- Security fundamentals aligned with CompTIA Security+
- Hands-on labs and simulated network environments
Students considering an associate-level cybersecurity degree in Ohio should verify:
- Regional accreditation
- Transfer agreements with four-year institutions
- Industry certification alignment
Ohio’s public community college system provides technical education pathways that can articulate into bachelor’s programs across the state’s higher education system.
- Program: Associate of Applied Science in Cyber Security & Computer Forensics
Credits: 61
Cost per credit: $126 in state | $230 out of state
Delivery method: Campus
Learn more: Program details - Program: Associate of Applied Science in Cybersecurity / Information Assurance Technology
CAE designation: CAE-CD
Credits: 61
Cost per credit: $175 in state | $323 out of state
Delivery method: Campus
Learn more: Program details - Program: Computer Science - Cybersecurity Major AAS
CAE designation: CAE-CD
Credits: 64-65
Cost per credit: $178 in state | $364 out of state
Delivery method: Campus
Learn more: Program details - Program: Associate of Applied Science in Cyber and Information Security
Credits: $159 in state | $336 out of state
Cost per credit: 64-65
Delivery method: Campus
Learn more: Program details - Program: Associate of Applied Science in Cyber Security
Credits: 63-65
Cost per credit: $173 in state | $345 out of state
Delivery method: Campus
Learn more: Program details - Program: Associate of Applied Science in Cyber Investigation Technology
CAE designation: CAE-CD
Credits: 61
Cost per credit: $136 in state | $339 out of state
Delivery method: Campus
Learn more: Program details - Program: Associate of Applied Science in Computer Technology - Networking & Cybersecurity
Credits: 64
Cost per credit: $192 in state | $366 out of state
Delivery method: Campus
Learn more: Program details - Program: Associate of Science in Cyber Security and Computer Forensics
Credits: 64
Cost per credit: $195 in state | $324 out of state
Delivery method: Online
Learn more: Program details - Program: Associate of Applied Science in Computer Information Systems
Credits: 63.5
Cost per credit: $194 in state | $388 out of state
Delivery method: Campus
Learn more: Program details - Program: Assoc. Information technology Network Security
Credits: 108
Cost per credit: $224
Delivery method: Campus
Learn more: Program details
Bachelor’s degrees
A bachelor’s degree is the most common credential for entry-level cybersecurity analyst roles.
In Ohio, students should evaluate bachelor’s programs based on:
- Dedicated cybersecurity coursework (secure coding, digital forensics, cloud security)
- Internship pipelines with government or private employers
- Participation in federally recognized cybersecurity education programs
Several Ohio institutions hold designation as National Centers of Academic Excellence in Cyber Defense (CAE-CD) through the NSA and DHS. Students should verify their current CAE status using the official CAE directory.
Ohio also has distinctive university-led cybersecurity initiatives:
- The University of Cincinnati’s Ohio Cyber Range Institute (OCRI) provides statewide cyber range infrastructure and training partnerships supporting education and workforce development.
- Wright State University’s National Center for Medical Readiness (NCMR) integrates cyber and emergency preparedness training within broader homeland security and defense contexts.
When evaluating cybersecurity schools in Ohio, students should prioritize programs with lab-based instruction, employer engagement, and applied learning.
- Program: Cybersecurity, B.S.
Credits: 120
Cost per credit: $924 in-state | $924 out-of-state
Delivery method: On-campus & online
Learn more: Program details - Program: BS in Cyber Operations
CAE designation: CAE-CD, CAE-CO
Credits: 128
Cost per credit: $280
Delivery method: Campus
Learn more: Program details - Program: Bachelors in Cyber Security
CAE designation: CAE-CD
Credits: 128
Cost per credit: 398
Delivery method: Online
Learn more: Program details - Program: Cybersecurity Bachelor’s Degree
Credits: 120
Cost per credit: $503
Delivery method: Online
Learn more: Program details
Master’s degrees
Graduate cybersecurity programs in Ohio are designed for:
- IT professionals advancing into security leadership roles
- Engineers transitioning into security architecture
- Students pursuing research or public-sector cybersecurity roles
Master’s programs may include:
- Advanced network defense
- Risk management and governance
- Cyber law and policy
- Digital forensics
- Applied capstone or research projects
Students should verify whether programs include employer partnerships, cyber range access, or funded research centers.
Campus-based master’s degrees
- Program: Master of Science degree with a major in Cyber Operations
CAE designation: CAE-R
Credits: 48
Delivery method: Campus
Learn more: Program details - Program: Master’s Programs in Cyber Security
Credits: 30
Cost per credit: $627 in-state | $1,101 out of state
Delivery method: Campus
Learn more: Program details - Program: Master of Science in Cyber Security
CAE designation: CAE-CD
Credits: 30
Cost per credit: $660 in-state | $1,125 out of state
Delivery method: Campus & online
Learn more: Program details
Online master’s degrees
- Program: M.S. in Cybersecurity
CAE designation: CAE-CD
Credits: 36
Cost per credit: $670
Delivery method: Online
GRE requirement: Not required
Learn more: Program details - Program: Master of Science Cyber Security
CAE designation: CAE-CD
Credits: 30
Cost per credit: $700
Delivery method: Online
GRE requirement: Not required
Learn more: Program details - Program: Master of Science in Cyber Security
CAE designation: CAE-CD
Credits: 30
Cost per credit: $660 in-state | $1,125 out of state
Delivery method: Campus & online
GRE requirement: Required
Learn more: Program details
Certifications and workforce programs
Ohio supports workforce development through both academic and state-led initiatives.
The Ohio Department of Job and Family Services provides information on in-demand occupations and training pathways. Students exploring short-term programs should confirm:
- Alignment with industry certifications
- Employer recognition
- Placement outcomes
Programs connected to cyber ranges or state workforce initiatives often provide more applied experience than classroom-only certificate programs.

Campus-based cybersecurity certifications
- Program: Cyber Security Certificate
Credits: 32
Cost per credit: $126 in state | $230 out of state
Delivery method: Campus
Learn more: Program details - Program: IT Security Stackable Certificate
CAE designation: CAE-CD
Credits: 24
Cost per credit: $178 in state | $364 out of state
Delivery method: Campus
Learn more: Program details - Program: Computer Forensics and Information Security Certificate
CAE designation: CAE-CD
Credits: 23
Cost per credit: $881 in state | $$1670 out of state
Delivery method: Campus
Learn more: Program details - Program: Computer Forensics and Information Security Undergraduate Certificate
CAE designation: CAE-CD
Credits: 23
Cost per credit: $714 in state | $1240 out of state
Delivery method: Campus
Learn more: Program details - Program: Computer Forensics and Information Security Certificate
CAE designation: CAE-CD
Credits: 23
Cost per credit: $714 in state | $1240 out of state
Delivery method: Campus
Learn more: Program details - Program: Digital Forensics and CompTIA+ Security Certification Preparation Certificate
Credits: 8
Cost per credit: $159 in state | $336 out of state
Delivery method: Campus
Learn more: Program details - Program: Cyber Security Fundamentals Certificate
Credits: 10
Cost per credit: $187 in state | $373 out of state
Delivery method: Campus
Learn more: Program details - Program: Security Tech Certificate
Credits: 27-28
Cost per credit: $173 in state | $345 out of state
Delivery method: Campus
Learn more: Program details - Program: Computer Security, Certificate
Credits: 21
Cost per credit: $800 in-state | $1,077 out of state
Delivery method: Campus
Learn more: Program details - Program: Cyber Operations Certificate
CAE designation: CAE-CD, CAE-CO
Credits: 18-20
Cost per credit: $746 in-state | $1,333 out of state
Delivery method: Campus
Learn more: Program details - Program: Cyber Security Analytics Undergraduate Certificate
CAE designation: CAE-CD
Credits: 12-16
Cost per credit: $464 in-state | $857 out of state
Delivery method: Campus
Learn more: Program details
Online cybersecurity certifications
- Program: Cybersecurity Certificate
CAE designation: CAE-CD
Duration: 31 weeks
Cost: $4,455
Delivery method: Online & Hybrid
Learn more: Program details - Program: Cyber Security Specialist (CSS)
Duration: 30-42 weeks
Cost: $587
Delivery method: Online
Learn more: Program details - Program: Graduate Certificate in Cybersecurity Offense and Defense
Credits: 12
Cost per credit: $756
Delivery method: Online
Learn more: Program details - Program: Cyber Investigation Certificate
CAE designation: CAE-CD
Credits: 33-34
Cost per credit: $136 in state | $339 out of state
Delivery method: Online
Learn more: Program details - Program: Cybersecurity Technician
Credits: 18
Cost per credit: $194 in-state | $381 out of state
Delivery method: Online
Learn more: Program details
Scholarship for Service (SFS)
The National Science Foundation’s CyberCorps®: Scholarship for Service (SFS) program funds cybersecurity education in exchange for post-graduation service in federal, state, or local government roles.
Ohio institutions periodically participate in SFS funding cycles. Students should verify current participating institutions through the official NSF SFS site, as participation status may change by award period.
Unique state cybersecurity initiatives
Ohio maintains statewide IT and cybersecurity governance through the State of Ohio Office of Information Technology (OIT), which oversees cybersecurity policy, enterprise IT security, and statewide cyber risk management.
In addition:
- The Ohio Cyber Range Institute (OCRI) provides shared cyber range infrastructure for K–12, higher education, and workforce partners across the state.
- State-supported cybersecurity competitions and workforce pipeline efforts are coordinated in partnership with public universities and regional employers.
These initiatives create structured pathways from education into government and private-sector cybersecurity roles.
Frequently asked questions about cybersecurity degrees in Ohio
CyberSeek reports thousands of active cybersecurity job postings in Ohio and provides a supply-demand ratio for the state workforce. For official employment counts, refer to the BLS state employment estimates for information security analysts.
According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, Information Security Analysts in Ohio earn a mean annual wage significantly above the statewide average wage. Students should consult the latest BLS release for updated figures.
There is no single “best” cybersecurity degree in Ohio. Students should prioritize:
– Accredited programs
– Hands-on labs or cyber range access
– Internship or employer engagement
– Alignment with CAE designation
Many institutions serving Ohio residents offer online or hybrid cybersecurity programs. Students should confirm modality, accreditation, and residency requirements directly with the institution.
Yes. Workforce-oriented certificate programs and technical training pathways are available. The Ohio Department of Job and Family Services provides guidance on in-demand occupations and approved training providers.
CyberSeek job posting data indicates common employer requests for certifications such as CompTIA Security+, CISSP, and CEH in Ohio.
Yes. CyberSeek demand signals and BLS employment data both indicate sustained demand for cybersecurity professionals in Ohio.
Yes. An associate degree can prepare students for entry-level IT and security roles and may transfer into a bachelor’s program within Ohio’s public university system.
Associate degree: about 2 years, Bachelor’s degree: about 4 years, and Master’s degree: typically 1–2 years
Ohio institutions have participated in NSF’s Scholarship for Service program. Students should verify current participation through the official NSF SFS directory.
Cybersecurity graduates in Ohio work in:
– State and local government
– Healthcare systems
– Financial services
– Manufacturing
– Defense and aerospace
Public-sector cybersecurity coordination is overseen by the Ohio Office of Information Technology.
Yes. Entry-level roles such as SOC analyst, security analyst I, and IT security specialist appear regularly in CyberSeek job postings for Ohio.
Sources
- CyberSeek | Cybersecurity Supply/Demand Heat Map | Accessed March 4, 2026
- Ohio Department of Job and Family Services | Labor Market Information | Accessed March 4, 2026
- U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics | Occupational Employment and Wage Statistics – Information Security Analysts | Accessed March 4, 2026
- U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics | Occupational Employment and Wage Statistics – Computer Systems Analysts | Accessed March 4, 2026
- National Centers of Academic Excellence in Cybersecurity | CAE Directory | Accessed March 4, 2026
- University of Cincinnati | Ohio Cyber Range Institute | Accessed March 4, 2026
- Wright State University | National Center for Medical Readiness | Accessed March 4, 2026
- National Science Foundation | CyberCorps®: Scholarship for Service (SFS) | Accessed March 4, 2026
- State of Ohio Office of Information Technology | Main page | Accessed March 4, 2026