This guide outlines the career path of a business information security officer (BISO), detailing necessary degrees, salary information, and potential positions.
Ad
cybersecurityguide.org is an advertising-supported site. Clicking in this box will show you programs related to your search from schools that compensate us. This compensation does not influence our school rankings, resource guides, or other information published on this site.
Featured Cybersecurity Training
| School Name | Program | More Info |
|---|---|---|
| Purdue Global | Online BS in Cybersecurity | website |
| UC Berkeley School of Information | Online Master’s in Cybersecurity | No GRE/GMAT Required | website |
| Arizona State University | Online BS in Information Technology - Cybersecurity | website |
| Southern New Hampshire University | Online BS in Cybersecurity or Online MS in Cybersecurity | website |
The BISO is vital in cybersecurity, bridging organizational goals with cyber threat protection in large entities. They collaborate with tech and business leaders to integrate cybersecurity into long-term planning.
BISOs act as intermediaries between security and operational teams, advising leaders and offering expertise on compliance, risk assessment, and data loss prevention. They ensure cybersecurity is integrated into new tech initiatives from the start, rather than being added on as an afterthought.
A BISO may also:
- Serve as the primary security contact for the board of directors
- Develop and oversee the implementation of security policies, procedures, and controls
- Conduct risk assessments and manage security incident response
- Monitor compliance with security regulations
- Manage security budgets
BISO skill set
It takes a diverse skill set to become an effective business information security officer. Some of those skills include:
- Strong business acumen: BISOs need to understand and speak the language of business. They must be able to clearly articulate the value of cybersecurity investments to business leaders who may not be familiar with the technical details.
- Strong technical skills: BISOs must have a deep understanding of cybersecurity technologies and how they can protect their organization’s assets. They should also be familiar with a wide range of IT systems and applications.
- Strong communication skills: BISOs must effectively communicate with both technical and non-technical staff. They must be able to translate complex technical concepts into plain English and present them in a way that decision-makers can understand.
- Understanding of risk management principles: BISOs must be able to identify, assess, and prioritize risks. They must also be familiar with the principles of risk management and how they apply to cybersecurity.
- Strong project management skills: BISOs must oversee projects from inception to completion, establishing objectives, timelines, and budgets, while adapting to emerging cyber threats. Success requires a profound understanding of both technology and business.
How to become a BISO
A common path to becoming a BISO involves studying a blend of science and management, including degrees in IT management, cybersecurity policy, and business administration with a focus on information security.
You’ll gain a strong, business-oriented foundation in IT and cybersecurity principles with these degrees. Coursework covers topics such as risk management, incident response, forensics, and network security.
Other popular degrees include a bachelor’s degree in computer science or information technology and a law degree with a focus on information security law.
Alternatively, there are many ways to get into the field without a traditional four-year degree. One way is via certifications or bootcamps. Bootcamps vary in length and can offer a more immersive, hands-on learning experience than traditional classroom instruction. They can also be more expensive than college courses. There are many types of certifications available, from entry-level to expert.
Certifications for business information security officers
- Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP): Offered by (ISC)², CISSP is one of the most popular and well-recognized certifications in the industry. The certificate covers a broad range of topics, including asset security, network security, access control, and cryptography.
- Certified Information Security Manager (CISM): Offered by ISACA, CISM is a popular certification that covers general security, risk management, communication, network security, operations, and security testing.
- CRISC: Offered by ISACA, CRISC is a certification that covers key domains of enterprise risk management: identification, assessment, control, mitigation, and monitoring.
- Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH): Offered by the EC-Council, CEH is a popular certification that covers topics such as corrective and protective countermeasures to protect systems from cyberattacks.
- CompTIA Security+: Offered by CompTIA, Security+ is a vendor-neutral certification that covers topics such as network security, cryptography, identity management, threats and vulnerabilities, and risk management.
What does a day in the life of a BISO look like?
The day-to-day duties of a BISO vary depending on the size and structure of the organization they work for.
On a day-to-day basis, a BISO may:
- Monitor security compliance
- Investigate security incidents
- Manage security awareness programs
- Train employees on security procedures
- Implement new security technologies
Some common challenges many BISOs face include:
- Getting buy-in from employees on security procedures
- Keeping up with the latest security threats
- Staying within budget
- Maintaining compliance with security regulations
Business information security officer job descriptions
Interested in learning more about some of the specific career roles in the Business Information Security Officer (BISO) field? Here are some common BISO jobs you might see mentioned in job descriptions:
Business information security officer
The Business Information Security Officer (BISO) upholds the organization’s security, collaborates with executive leadership on a risk management program, advises on security best practices, oversees security training, and investigates security incidents.
Other responsibilities include:
- Creating and maintaining security policies and procedures
- Conducting risk assessments
- Investigating security incidents
- Implementing new security technologies
Qualifications needed:
- Bachelor’s degree in computer science or related field
- Minimum of eight years of experience in information security
- CISSP, CISM, or CRISC certification preferred
Business unit information security officer
The business unit information security officer directs the company’s Information Security program and strategy, manages business operations & technology security issues, represents local security concerns, provides updates on security measure efficacy, and ensures compliance across business, IT, and security departments.
Other responsibilities include:
- Directing the company’s information security program
- Managing security issues related to business operations and technology (BOT)
- Acting as an information security representative in local security concerns
- Providing read-outs on the efficiency of security measures
Qualifications needed:
- Master’s degree in information systems or related field
- Minimum of ten years of experience in Information Security
- CISSP, CISM, or CRISC certification preferred
Director of business information security
The director of business information security (BIS) leads the development and enhancement of systems and processes to safeguard the company’s information assets, ensuring their confidentiality, integrity, and availability. The director of BIS reports to the chief information officer (CIO).
Responsibilities include:
- Developing and maintaining the business information security program, including the development of policies, procedures, and standards
- Leading incident response efforts in the event of a data breach or other security incident
- Working with business units to ensure compliance with security policies and procedures
- Conducting risk assessments and security audits
- Researching new security technologies and trends
- Providing guidance and support to business units on security-related issues
- Developing and delivering security awareness training programs
- Maintaining relationships with law enforcement, government agencies, and other stakeholders
- Coordinating with the IT department on technical security issues
Qualifications needed:
- Proven experience in developing and leading business information security programs
- Strong understanding of security principles, technologies, and processes
- Experience with incident response, risk management, and security audits
- Excellent communication and interpersonal skills
- Ability to work independently and take initiative
- Flexibility and adaptability
BISO salary ranges
According to Salary.com, the average salary range for a business security officer is between $67,817 and $94,861 as of 2025.
Like other careers, this range can depend on several factors, including geography, experience, and level of education.
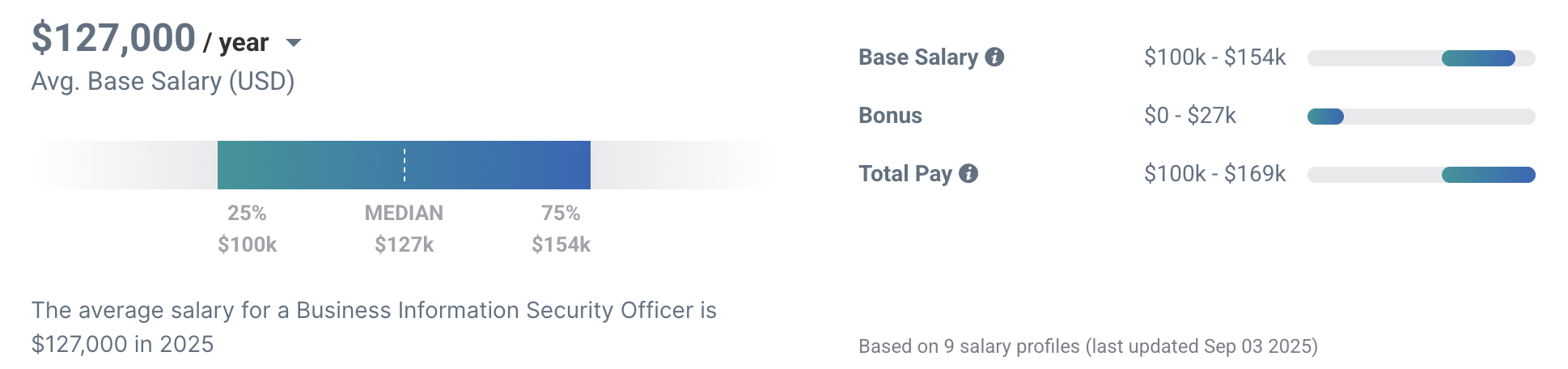
The site Payscale.com reports that the average BISO salary is $127,000, which is the midpoint of a range that takes into account a variety of factors.
Final thoughts
The role of the business information security officer is constantly growing as new technologies and threats emerge. Therefore, individuals in this role need to keep up with industry trends and best practices.
Business Information Security Officers require a thorough understanding of technology and business processes and must effectively communicate the business advantages of cybersecurity to stakeholders throughout the organization.
Frequently asked questions
A business information security officer (BISO) is a senior-level executive responsible for overseeing and managing the information security and cybersecurity strategy and operations of a business or organization.
Earn a degree in a mix of science and management this includes information technology management, cybersecurity policy and management, and business administration with an information security focus to obtain a business-oriented foundation in IT and cybersecurity principles. Another way to get into the field without a traditional four-year degree is through certifications or bootcamps.
Advancement can come through gaining additional certifications, pursuing higher education in cybersecurity or business management, and accumulating experience in managing security programs in various business contexts.
BISOs are responsible for developing and maintaining the organization’s security posture, managing risk, ensuring compliance, overseeing security training, and investigating security incidents.